Please note that this repository has been deprecated and is no longer actively maintained by Polyverse Corporation. It may be removed in the future, but for now remains public for the benefit of any users.
Importantly, as the repository has not been maintained, it may contain unpatched security issues and other critical issues. Use at your own risk.
While it is not maintained, we would graciously consider any pull requests in accordance with our Individual Contributor License Agreement. https://github.com/polyverse/contributor-license-agreement
For any other issues, please feel free to contact info@polyverse.com
Netdata is distributed, real-time, performance and health monitoring for systems and applications. It is a highly optimized monitoring agent you install on all your systems and containers.
Netdata provides unparalleled insights, in real-time, of everything happening on the systems it runs (including web servers, databases, applications), using highly interactive web dashboards. It can run autonomously, without any third party components, or it can be integrated to existing monitoring tool chains (Prometheus, Graphite, OpenTSDB, Kafka, Grafana, etc).
Netdata is fast and efficient, designed to permanently run on all systems (physical & virtual servers, containers, IoT devices), without disrupting their core function.
Netdata is free, open-source software and it currently runs on Linux, FreeBSD, and MacOS.
Netdata is not hosted by the CNCF but is the 3rd most starred open-source project in the Cloud Native Computing Foundation (CNCF) landscape.
People get addicted to Netdata.
Once you use it on your systems, there is no going back! You have been warned...
- How it looks - have a quick look at it
- User base - who uses Netdata?
- Quick Start - try it now on your systems
- Why Netdata - why people love Netdata, how it compares with other solutions
- News - latest news about Netdata
- How it works - high level diagram of how Netdata works
- infographic - everything about Netdata, in a page
- Features - what features does it have
- Visualization - unique visualization features
- What does it monitor - which metrics it collects
- Documentation - read the docs
- Community - discuss with others and get support
- License - check the license of Netdata
- Is it any good? - Yes
- Is it awesome? - Yes
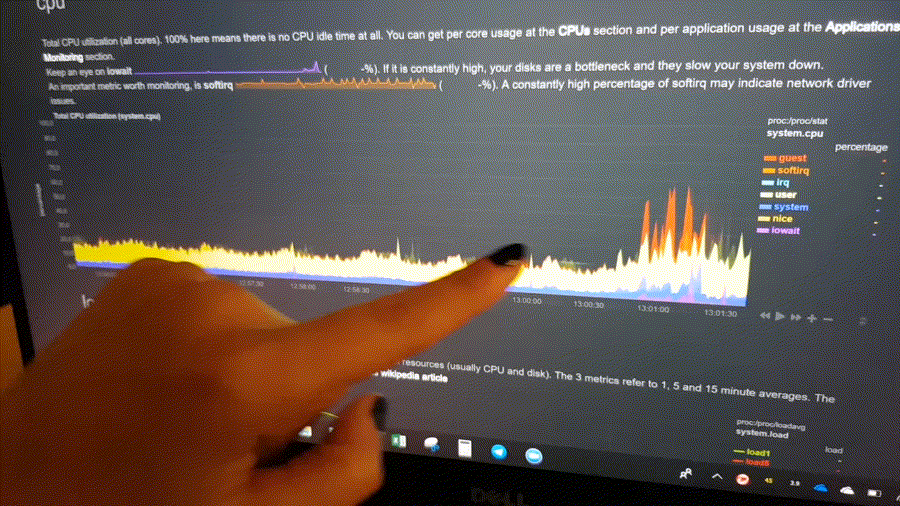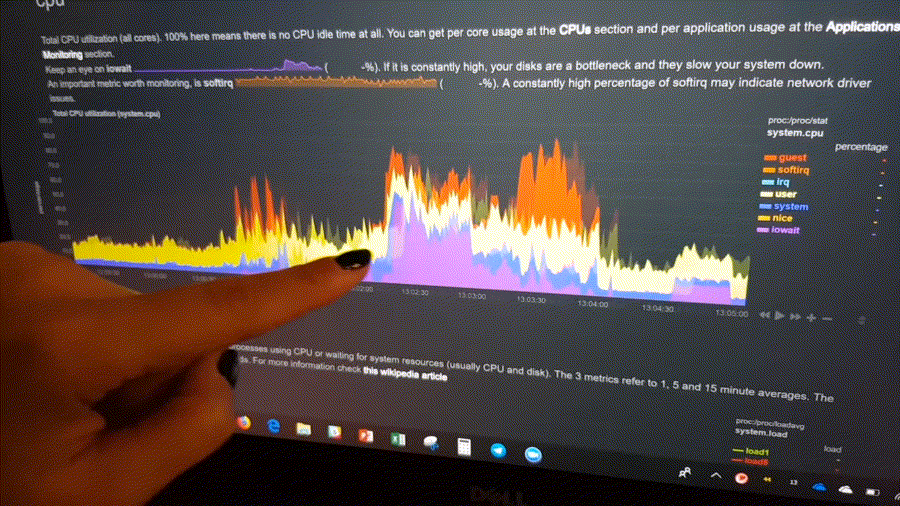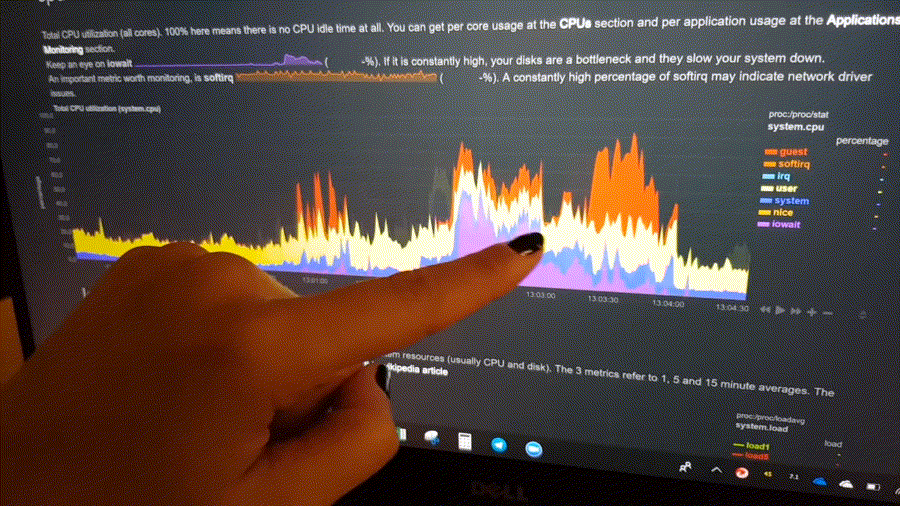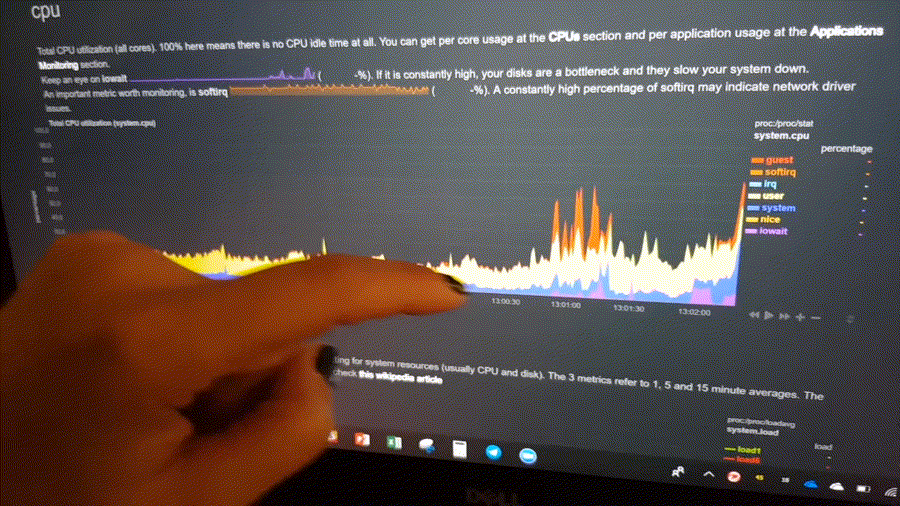
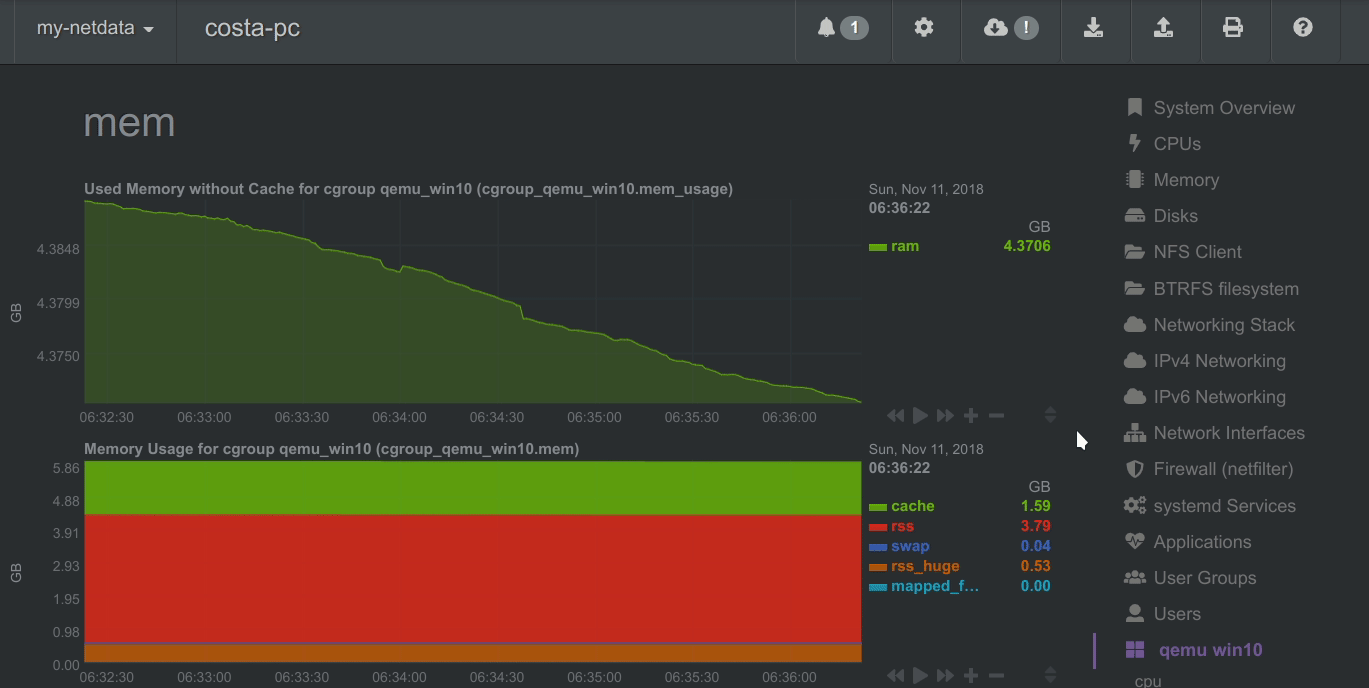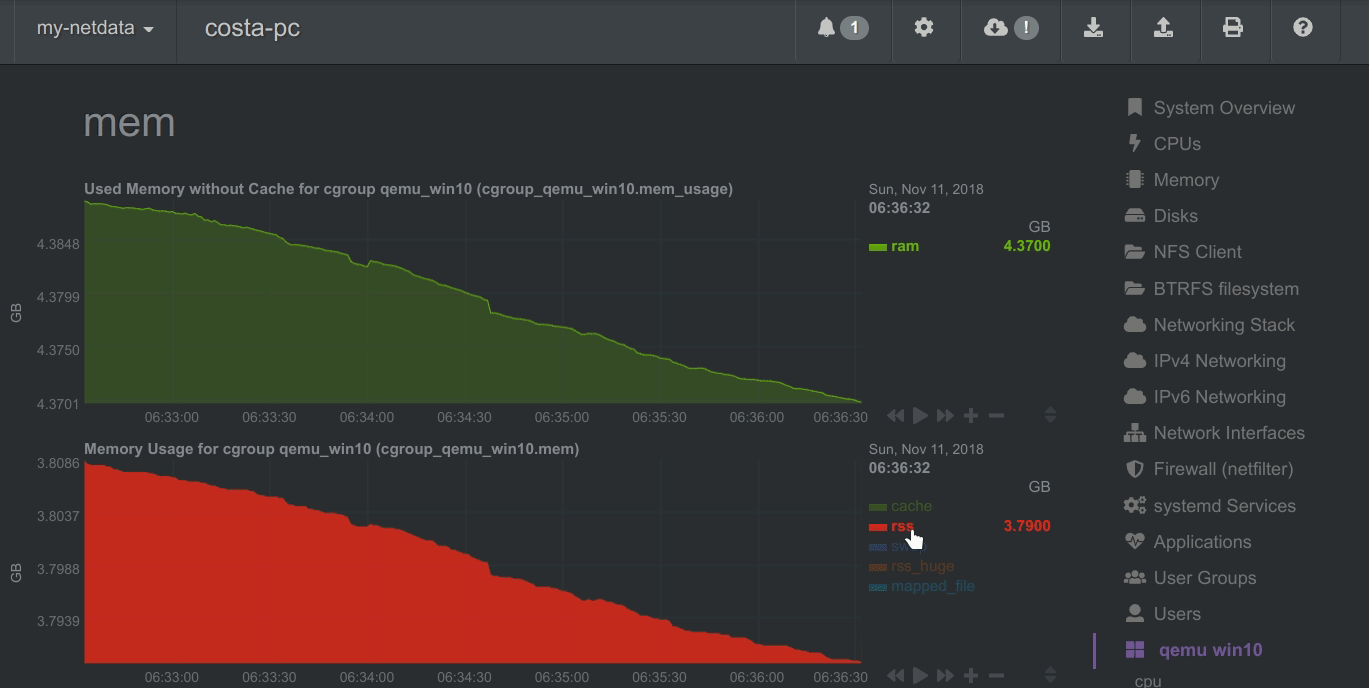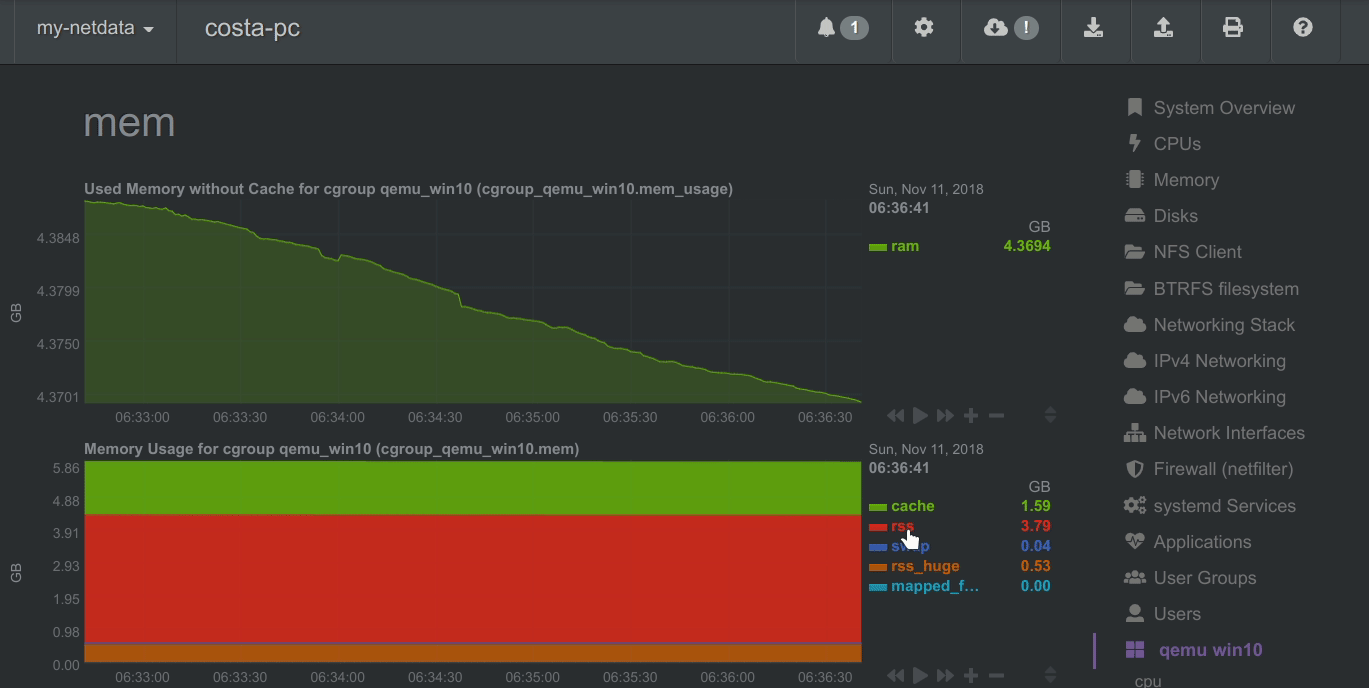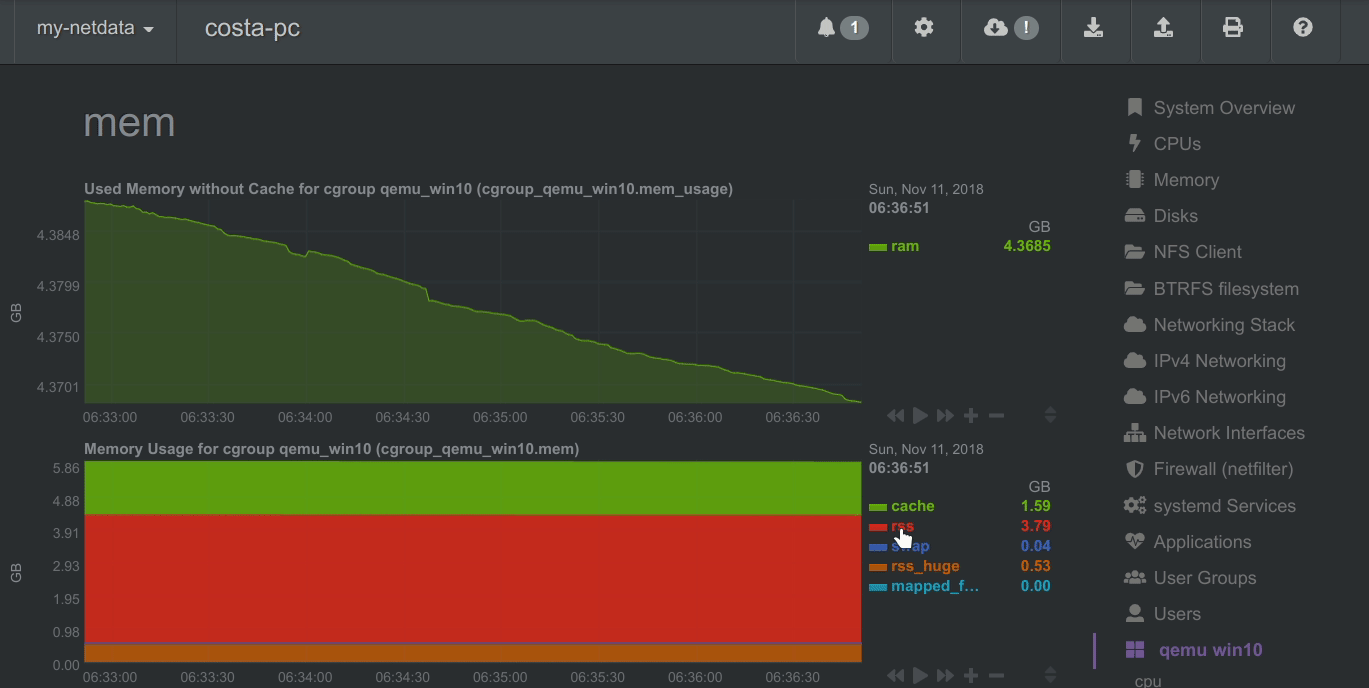
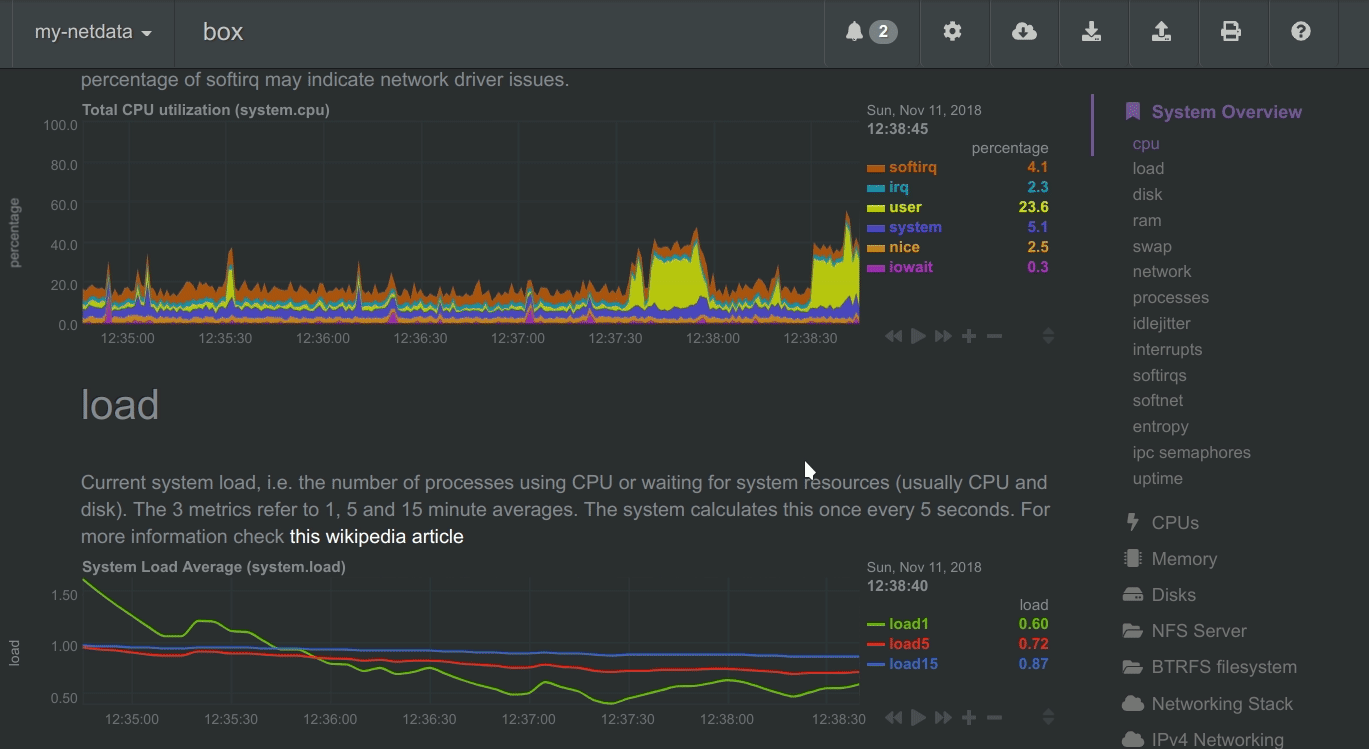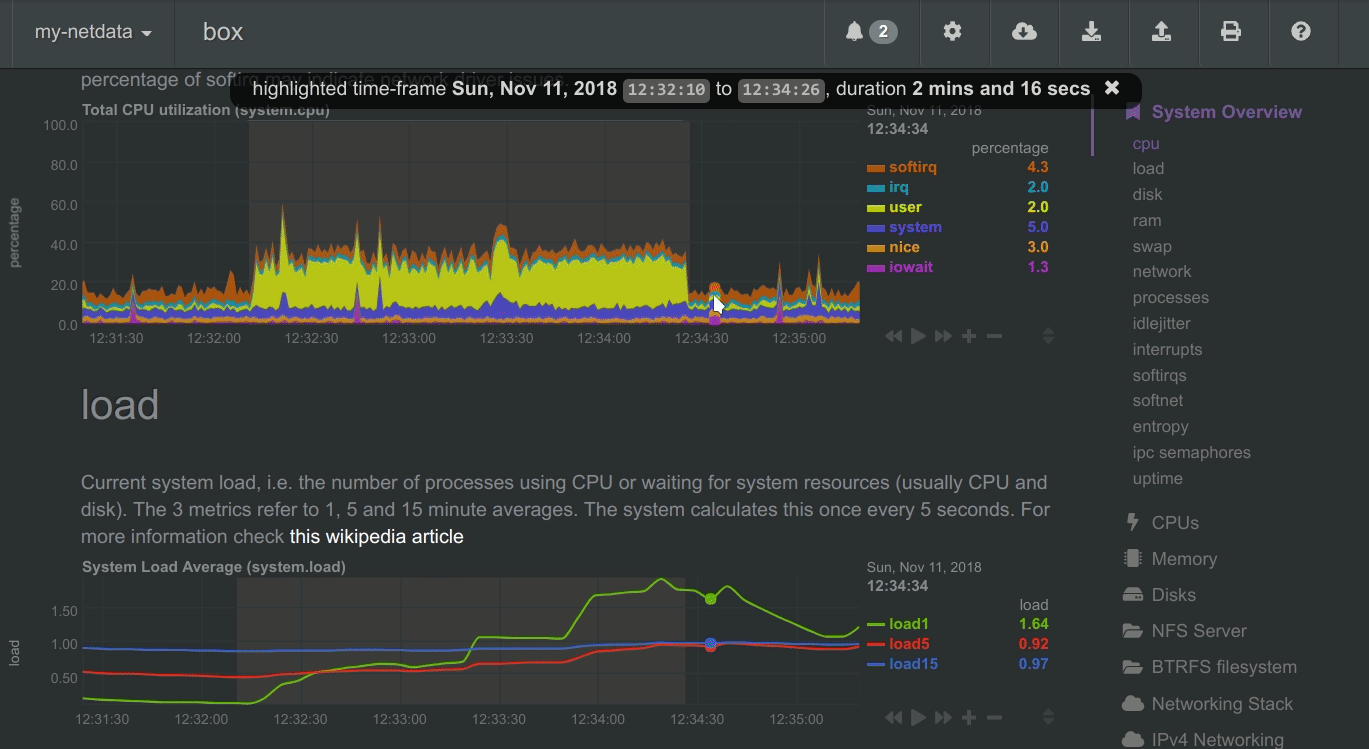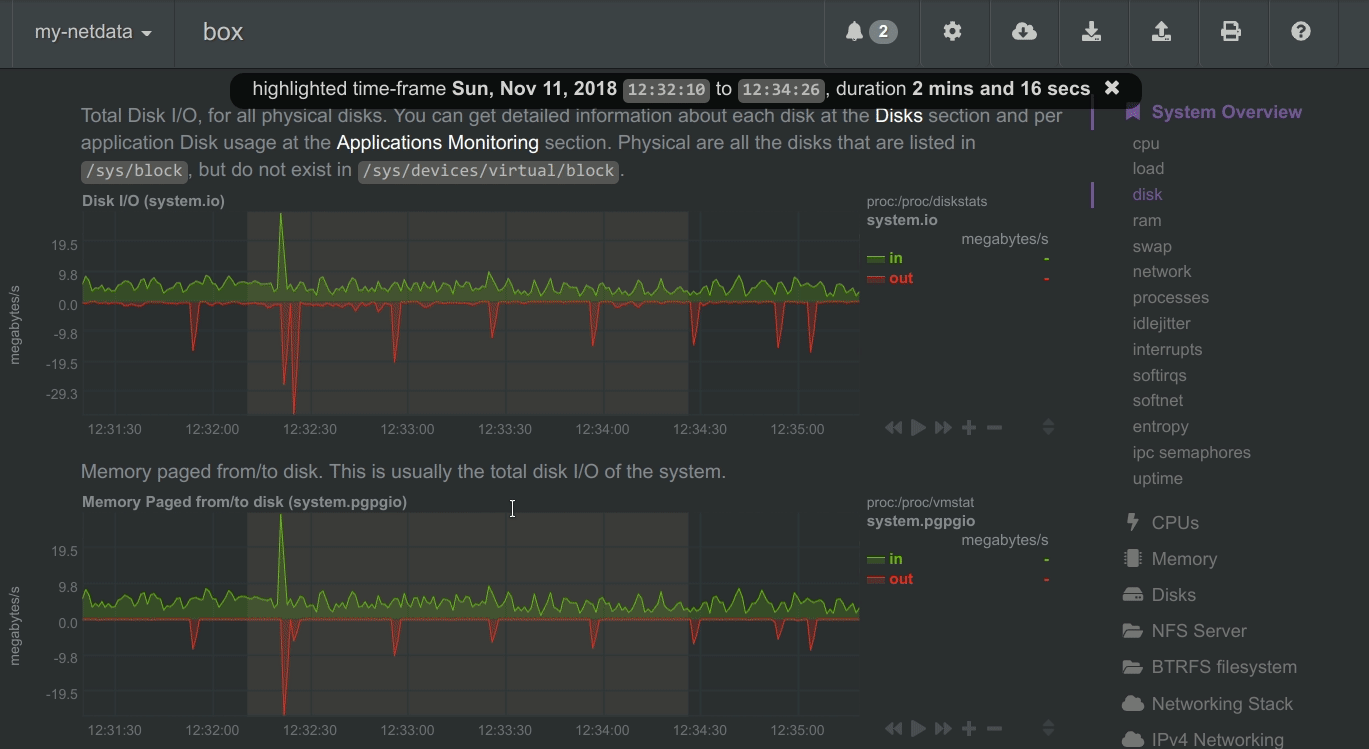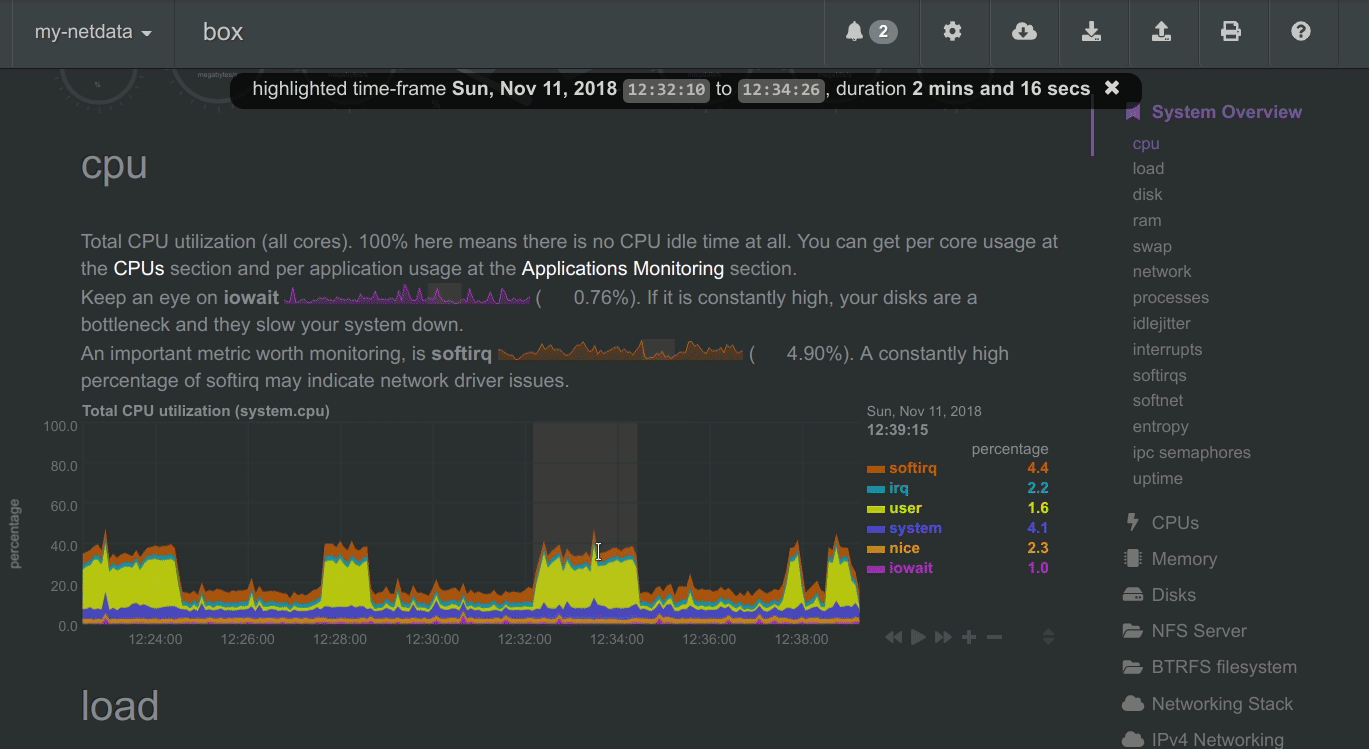
The following animated image, shows the top part of a typical Netdata dashboard.
A typical Netdata dashboard, in 1:1 timing. Charts can be panned by dragging them, zoomed in/out with SHIFT + mouse wheel, an area can be selected for zoom-in with SHIFT + mouse selection. Netdata is highly interactive and real-time, optimized to get the work done!
We have a few online demos to experience it live: https://my-netdata.io
Netdata is used by hundreds of thousands of users all over the world. Check our GitHub watchers list. You will find people working for Amazon, Atos, Baidu, Cisco Systems, Citrix, Deutsche Telekom, DigitalOcean, Elastic, EPAM Systems, Ericsson, Google, Groupon, Hortonworks, HP, Huawei, IBM, Microsoft, NewRelic, Nvidia, Red Hat, SAP, Selectel, TicketMaster, Vimeo, and many more!
We provide docker images for the most common architectures. These are statistics reported by docker hub:
When you install multiple Netdata, they are integrated into one distributed application, via a Netdata registry. This is a web browser feature and it allows us to count the number of unique users and unique Netdata servers installed. The following information comes from the global public Netdata registry we run:
You can quickly install Netdata on a Linux box (physical, virtual, container, IoT) with the following command:
# make sure you run `bash` for your shell
bash
# install Netdata, directly from github sources
bash <(curl -Ss https://my-netdata.io/kickstart.sh)The above command will:
- install any required packages on your system (it will ask you to confirm before doing so),
- compile it, install it and start it
More installation methods and additional options can be found at the installation page.
To try Netdata in a docker container, run this:
docker run -d --name=netdata \
-p 19999:19999 \
-v /proc:/host/proc:ro \
-v /sys:/host/sys:ro \
-v /var/run/docker.sock:/var/run/docker.sock:ro \
--cap-add SYS_PTRACE \
--security-opt apparmor=unconfined \
netdata/netdata
For more information about running Netdata in docker, check the docker installation page.
From Netdata v1.12 and above, anonymous usage information is collected by default and sent to Google Analytics. To read more about the information collected and how to opt-out, check the anonymous statistics page.
Netdata has a quite different approach to monitoring.
Netdata is a monitoring agent you install on all your systems. It is:
- a metrics collector - for system and application metrics (including web servers, databases, containers, etc)
- a time-series database - all stored in memory (does not touch the disks while it runs)
- a metrics visualizer - super fast, interactive, modern, optimized for anomaly detection
- an alarms notification engine - an advanced watchdog for detecting performance and availability issues
All the above, are packaged together in a very flexible, extremely modular, distributed application.
This is how Netdata compares to other monitoring solutions:
| Netdata | others (open-source and commercial) |
|---|---|
| High resolution metrics (1s granularity) | Low resolution metrics (10s granularity at best) |
| Monitors everything, thousands of metrics per node | Monitor just a few metrics |
| UI is super fast, optimized for anomaly detection | UI is good for just an abstract view |
| Meaningful presentation, to help you understand the metrics | You have to know the metrics before you start |
| Install and get results immediately | Long preparation is required to get any useful results |
| Use it for troubleshooting performance problems | Use them to get statistics of past performance |
| Kills the console for tracing performance issues | The console is always required for troubleshooting |
| Requires zero dedicated resources | Require large dedicated resources |
Netdata is open-source, free, super fast, very easy, completely open, extremely efficient, flexible and integrate-able.
It has been designed by SysAdmins, DevOps and Developers for troubleshooting performance problems, not just visualize metrics.
May 21st, 2019 - Netdata v1.15.0 released!
Release v1.15.0 contains 11 bug fixes and 30 improvements.
We are very happy and proud to be able to include two major improvements in this release: The aggregated node view and the new database engine.
Aggregated node view
The No. 1 request from our community has been a better way to view and manage their Netdata installations, via an aggregated view. The node menu with the simple list of hosts on the agent UI just didn't do it for people with hundreds, or thousands of instances. This release introduces the node view, which uses the power of Netdata Cloud to deliver powerful views of a Netdata-based monitoring infrastructure. You can read more about Netdata Cloud and the future of Netdata here.
New database engine
Historically, Netdata has required a lot of memory for long-term metrics storage. To mitigate this we've been building a new DB engine for several months and will continue improving until it can become the default memory mode for new Netdata installations. The version included in release v1.15.0 already permits longer-term storage of compressed data and we'll continue reducing the required memory in following releases.
Other major additions
We have added support for the AWS Kinesis backend and new collectors for OpenVPN, the Tengine web server, ScaleIO (VxFlex OS), ioping-like latency metrics and Energi Core node instances.
We now have a new, "text-only" chart type, cpu limits for v2 cgroups, docker swarm metrics and improved documentation.
We continued improving the Kubernetes helmchart with liveness probes for slaves, persistence options, a fix for a Cannot allocate memory issue and easy configuration for the kubelet, kube-proxy and coredns collectors.
Finally, we built a process to quickly replace any problematic nightly builds and added more automated CI tests to prevent such builds from being published in the first place.
Apr 26th, 2019 - Netdata v1.14.0 released!
Release 1.14 contains 14 bug fixes and 24 improvements.
The release introduces major additions to Kubernetes monitoring, with tens of new charts for Kubelet, kube-proxy and coredns metrics, as well as significant improvements to the Netdata helm chart.
Two new collectors were added, to monitor Docker hub and Docker engine metrics.
Finally, v1.14 adds support for version 2 cgroups, OpenLDAP over TLS, NVIDIA SMI free and per process memory and configurable syslog facilities.
Mar 14th, 2019 - Netdata v1.13.0 released!
Release 1.13.0 contains 14 bug fixes and 8 improvements.
Netdata has taken the first step into the world of Kubernetes, with a beta version of a Helm chart for deployment to a k8s cluster and proper naming of the cgroup containers. We have big plans for Kubernetes, so stay tuned!
A major refactoring of the python.d plugin has resulted in a dramatic decrease of the required memory, making Netdata even more resource efficient.
We also added charts for IPC shared memory segments and total memory used.
Feb 28th, 2019 - Netdata v1.12.2 released!
Patch release 1.12.2 contains 7 bug fixes and 4 improvements.
The main motivation behind a new patch release is the introduction of a stable release channel. A "stable" installation and update channel was always on our roadmap, but it became a necessity when we realized that our users in China could not use the nightly releases published on Google Cloud. The "stable" channel is based on our official GitHub releases and uses assets hosted on GitHub.
We are also introducing a new Oracle DB collector module, implemented in Python.
Feb 21st, 2019 - Netdata v1.12.1 released!
Patch release 1.12.1 contains 22 bug fixes and 8 improvements.
Feb 14th, 2019 - Netdata v1.12.0 released!
Release 1.12 is made out of 211 pull requests and 22 bug fixes. The key improvements are:
- Introducing
netdata.cloud, the free Netdata service for all Netdata users - High performance plugins with go.d.plugin (data collection orchestrator written in Go)
- 7 new data collectors and 11 rewrites of existing data collectors for improved performance
- A new management API for all Netdata servers
- Bind different functions of the Netdata APIs to different ports
- Improved installation and updates
Nov 22nd, 2018 - Netdata v1.11.1 released!
- Improved internal database to support values above 64bit.
- New data collection plugins:
openldap,tor,nvidia_smi. - Improved data collection plugins: Netdata now supports monitoring network interface aliases,
smartd_log,cpufreq,sensors. - Health monitoring improvements: network interface congestion alarm restored,
alerta.io,conntrack_max. my-netdatamenu has been refactored.- Packaging:
openrcservice definition got a few improvements.
Sep 18, 2018 - Netdata has its own organization
Netdata used to be a firehol.org project, accessible as firehol/netdata.
Netdata now has its own github organization netdata, so all github URLs are now netdata/netdata. The old github URLs, repo clones, forks, etc redirect automatically to the new repo.
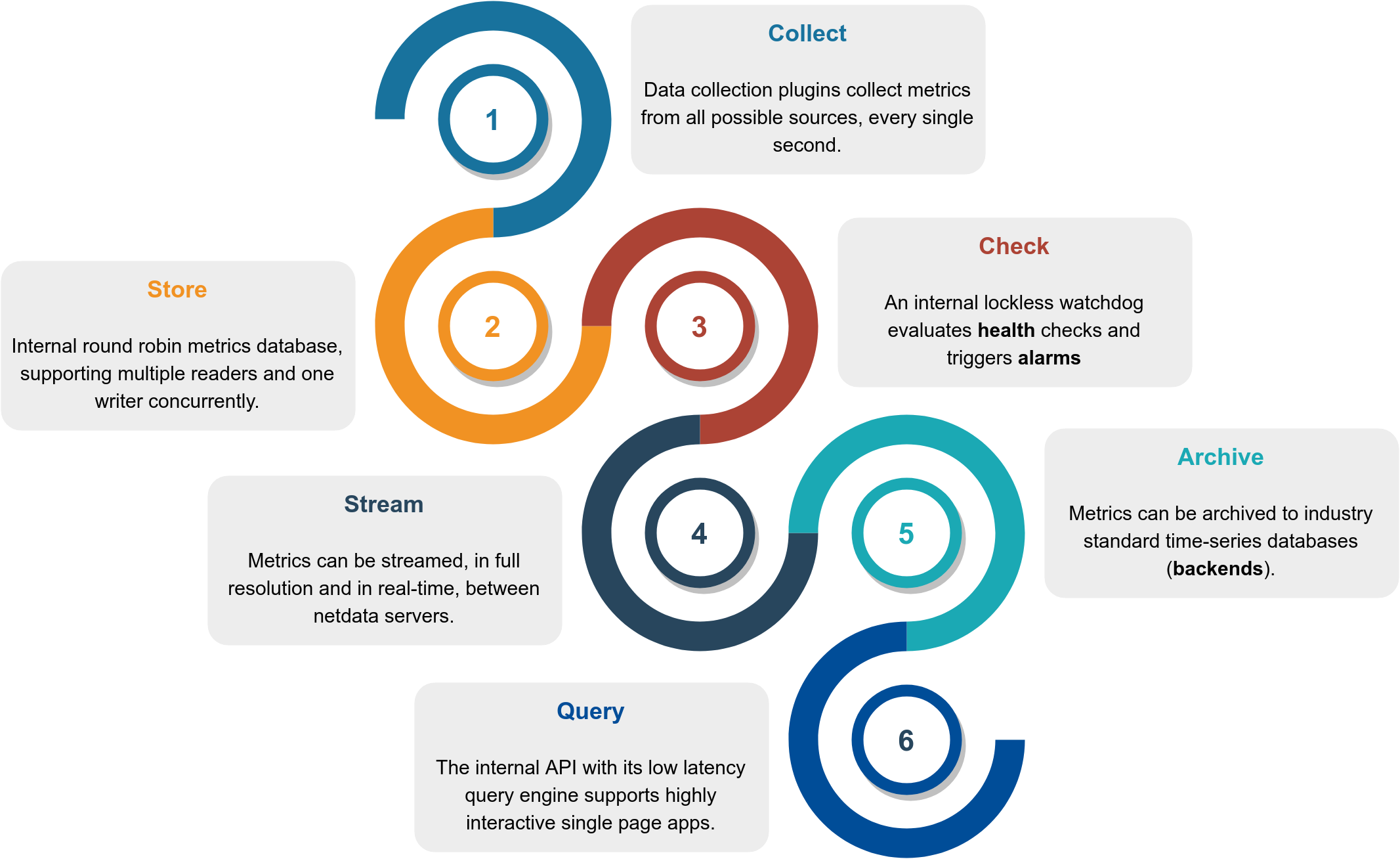
Netdata is a highly efficient, highly modular, metrics management engine. Its lockless design makes it ideal for concurrent operations on the metrics.
This is how it works:
| Function | Description | Documentation |
|---|---|---|
| Collect | Multiple independent data collection workers are collecting metrics from their sources using the optimal protocol for each application and push the metrics to the database. Each data collection worker has lockless write access to the metrics it collects. | collectors |
| Store | Metrics are stored in RAM in a round robin database (ring buffer), using a custom made floating point number for minimal footprint. | database |
| Check | A lockless independent watchdog is evaluating health checks on the collected metrics, triggers alarms, maintains a health transaction log and dispatches alarm notifications. | health |
| Stream | An lockless independent worker is streaming metrics, in full detail and in real-time, to remote Netdata servers, as soon as they are collected. | streaming |
| Archive | A lockless independent worker is down-sampling the metrics and pushes them to backend time-series databases. | backends |
| Query | Multiple independent workers are attached to the internal web server, servicing API requests, including data queries. | web/api |
The result is a highly efficient, low latency system, supporting multiple readers and one writer on each metric.
This is a high level overview of Netdata feature set and architecture. Click it to to interact with it (it has direct links to documentation).
This is what you should expect from Netdata:
- 1s granularity - the highest possible resolution for all metrics.
- Unlimited metrics - collects all the available metrics, the more the better.
- 1% CPU utilization of a single core - it is super fast, unbelievably optimized.
- A few MB of RAM - by default it uses 25MB RAM. You size it.
- Zero disk I/O - while it runs, it does not load or save anything (except
errorandaccesslogs). - Zero configuration - auto-detects everything, it can collect up to 10000 metrics per server out of the box.
- Zero maintenance - You just run it, it does the rest.
- Zero dependencies - it is even its own web server, for its static web files and its web API (though its plugins may require additional libraries, depending on the applications monitored).
- Scales to infinity - you can install it on all your servers, containers, VMs and IoTs. Metrics are not centralized by default, so there is no limit.
- Several operating modes - Autonomous host monitoring (the default), headless data collector, forwarding proxy, store and forward proxy, central multi-host monitoring, in all possible configurations. Each node may have different metrics retention policy and run with or without health monitoring.
- Sophisticated alerting - comes with hundreds of alarms, out of the box! Supports dynamic thresholds, hysteresis, alarm templates, multiple role-based notification methods.
- Notifications: alerta.io, amazon sns, discordapp.com, email, flock.com, irc, kavenegar.com, messagebird.com, pagerduty.com, prowl, pushbullet.com, pushover.net, rocket.chat, slack.com, smstools3, syslog, telegram.org, twilio.com, web and custom notifications.
- time-series dbs - can archive its metrics to
graphite,opentsdb,prometheus, json document DBs, in the same or lower resolution (lower: to prevent it from congesting these servers due to the amount of data collected).
- Stunning interactive dashboards - mouse, touchpad and touch-screen friendly in 2 themes:
slate(dark) andwhite. - Amazingly fast visualization - responds to all queries in less than 1 ms per metric, even on low-end hardware.
- Visual anomaly detection - the dashboards are optimized for detecting anomalies visually.
- Embeddable - its charts can be embedded on your web pages, wikis and blogs. You can even use Atlassian's Confluence as a monitoring dashboard.
- Customizable - custom dashboards can be built using simple HTML (no javascript necessary).
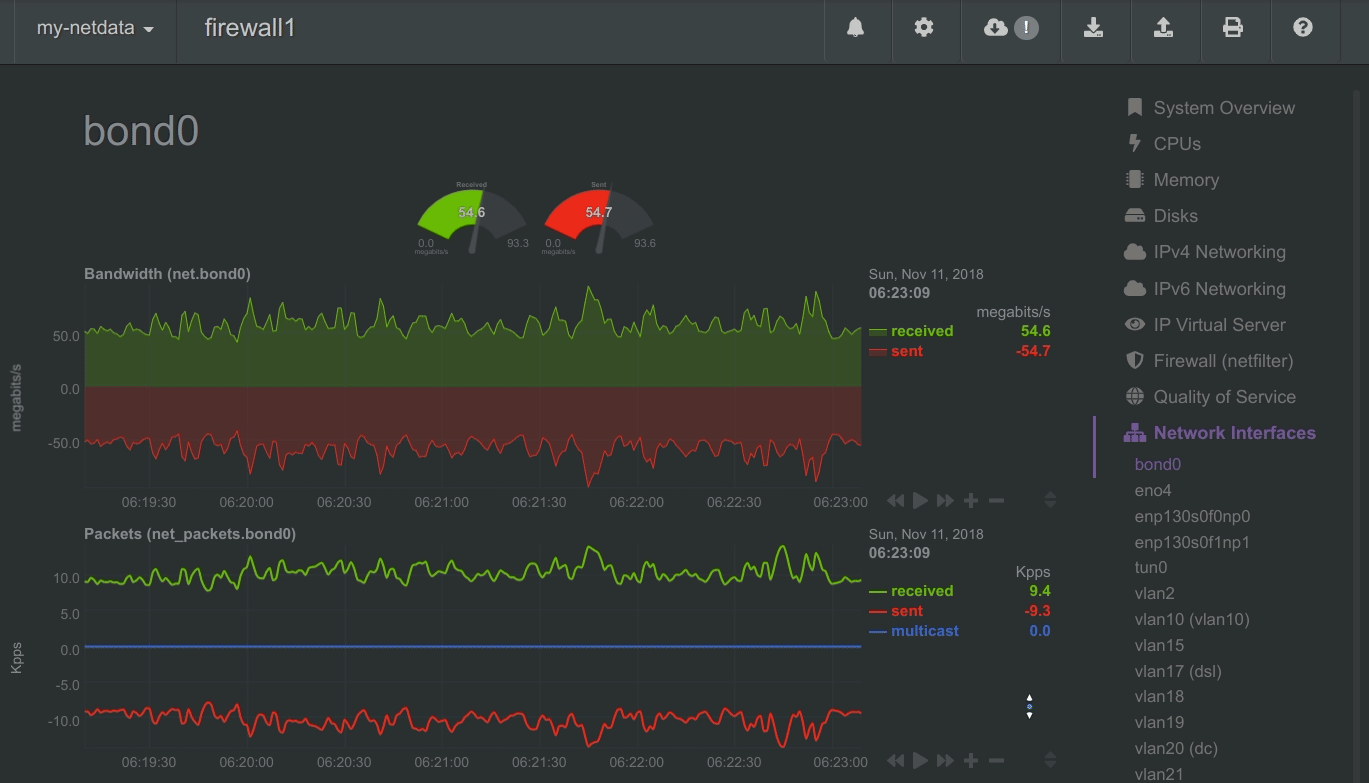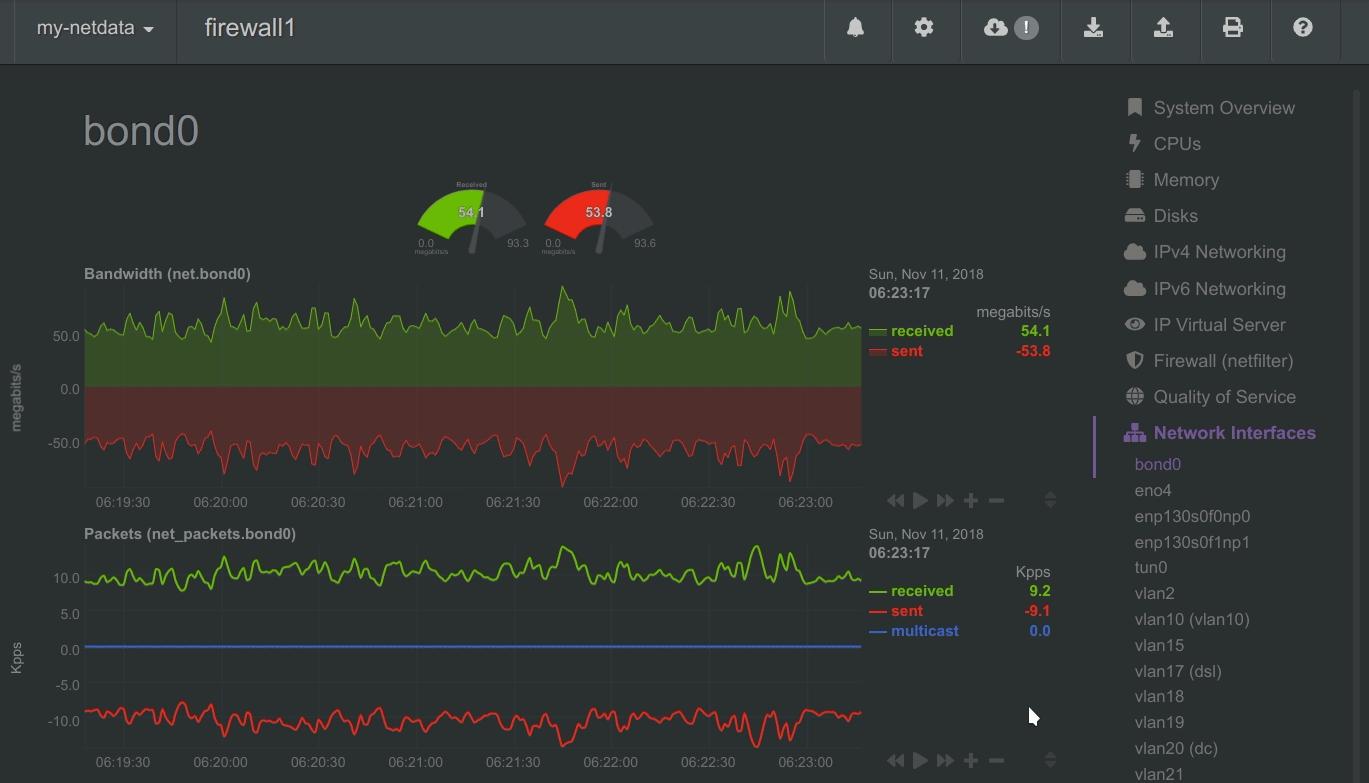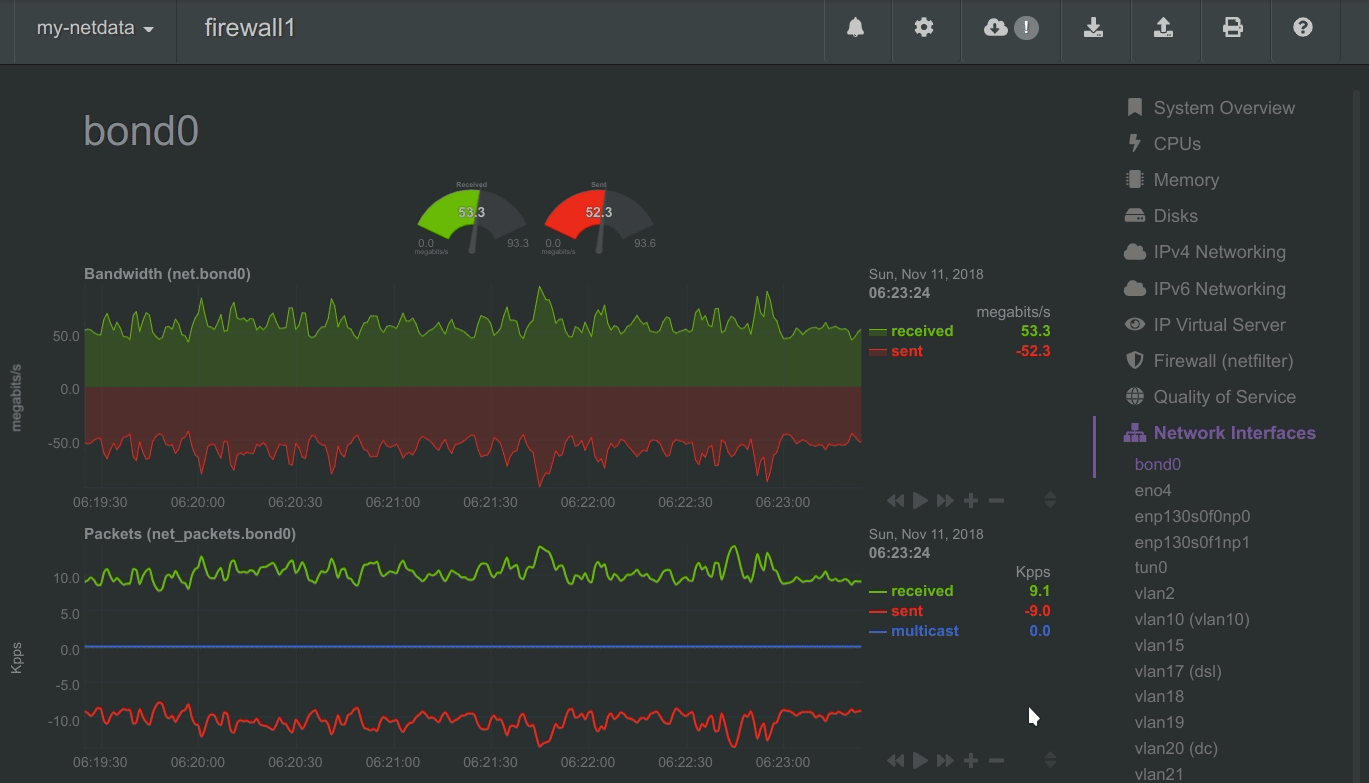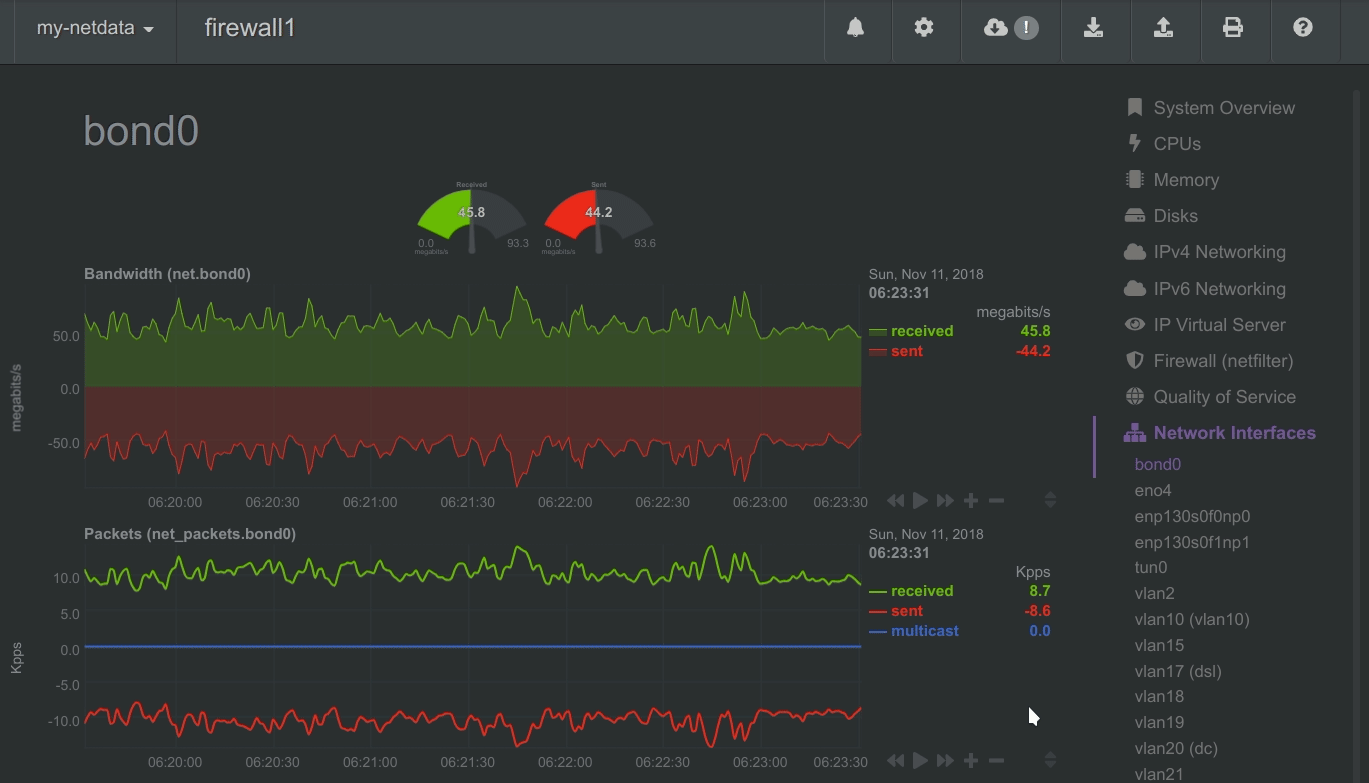
To improve clarity on charts, Netdata dashboards present positive values for metrics representing read, input, inbound, received and negative values for metrics representing write, output, outbound, sent.
Netdata charts showing the bandwidth and packets of a network interface. received is positive and sent is negative.
Netdata charts automatically zoom vertically, to visualize the variation of each metric within the visible time-frame.
A zero based stacked chart, automatically switches to an auto-scaled area chart when a single dimension is selected.
Charts on Netdata dashboards are synchronized to each other. There is no master chart. Any chart can be panned or zoomed at any time, and all other charts will follow.
Charts are panned by dragging them with the mouse. Charts can be zoomed in/out withSHIFT + mouse wheel while the mouse pointer is over a chart.
The visible time-frame (pan and zoom) is propagated from Netdata server to Netdata server, when navigating via the node menu.
To improve visual anomaly detection across charts, the user can highlight a time-frame (by pressing ALT + mouse selection) on all charts.
A highlighted time-frame can be given by pressing ALT + mouse selection on any chart. Netdata will highlight the same range on all charts.
Highlighted ranges are propagated from Netdata server to Netdata server, when navigating via the node menu.
Netdata data collection is extensible - you can monitor anything you can get a metric for. Its Plugin API supports all programing languages (anything can be a Netdata plugin, BASH, python, perl, node.js, java, Go, ruby, etc).
- For better performance, most system related plugins (cpu, memory, disks, filesystems, networking, etc) have been written in
C. - For faster development and easier contributions, most application related plugins (databases, web servers, etc) have been written in
python.
- statsd - Netdata is a fully featured statsd server.
- Go expvar - collects metrics exposed by applications written in the Go programming language using the expvar package.
- Spring Boot - monitors running Java Spring Boot applications that expose their metrics with the use of the Spring Boot Actuator included in Spring Boot library.
- uWSGI - collects performance metrics from uWSGI applications.
- CPU Utilization - total and per core CPU usage.
- Interrupts - total and per core CPU interrupts.
- SoftIRQs - total and per core SoftIRQs.
- SoftNet - total and per core SoftIRQs related to network activity.
- CPU Throttling - collects per core CPU throttling.
- CPU Frequency - collects the current CPU frequency.
- CPU Idle - collects the time spent per processor state.
- IdleJitter - measures CPU latency.
- Entropy - random numbers pool, using in cryptography.
- Interprocess Communication - IPC - such as semaphores and semaphores arrays.
- ram - collects info about RAM usage.
- swap - collects info about swap memory usage.
- available memory - collects the amount of RAM available for userspace processes.
- committed memory - collects the amount of RAM committed to userspace processes.
- Page Faults - collects the system page faults (major and minor).
- writeback memory - collects the system dirty memory and writeback activity.
- huge pages - collects the amount of RAM used for huge pages.
- KSM - collects info about Kernel Same Merging (memory dedupper).
- Numa - collects Numa info on systems that support it.
- slab - collects info about the Linux kernel memory usage.
- block devices - per disk: I/O, operations, backlog, utilization, space, etc.
- BCACHE - detailed performance of SSD caching devices.
- DiskSpace - monitors disk space usage.
- mdstat - software RAID.
- hddtemp - disk temperatures.
- smartd - disk S.M.A.R.T. values.
- device mapper - naming disks.
- Veritas Volume Manager - naming disks.
- megacli - adapter, physical drives and battery stats.
- adaptec_raid - logical and physical devices health metrics.
- ioping - to measure disk read/write latency.
- BTRFS - detailed disk space allocation and usage.
- Ceph - OSD usage, Pool usage, number of objects, etc.
- NFS file servers and clients - NFS v2, v3, v4: I/O, cache, read ahead, RPC calls
- Samba - performance metrics of Samba SMB2 file sharing.
- ZFS - detailed performance and resource usage.
- Network Stack - everything about the networking stack (both IPv4 and IPv6 for all protocols: TCP, UDP, SCTP, UDPLite, ICMP, Multicast, Broadcast, etc), and all network interfaces (per interface: bandwidth, packets, errors, drops).
- Netfilter - everything about the netfilter connection tracker.
- SynProxy - collects performance data about the linux SYNPROXY (DDoS).
- NFacct - collects accounting data from iptables.
- Network QoS - the only tool that visualizes network
tcclasses in real-time - FPing - to measure latency and packet loss between any number of hosts.
- ISC dhcpd - pools utilization, leases, etc.
- AP - collects Linux access point performance data (
hostapd). - SNMP - SNMP devices can be monitored too (although you will need to configure these).
- port_check - checks TCP ports for availability and response time.
- OpenVPN - collects status per tunnel.
- LibreSwan - collects metrics per IPSEC tunnel.
- Tor - collects Tor traffic statistics.
- System Processes - running, blocked, forks, active.
- Applications - by grouping the process tree and reporting CPU, memory, disk reads, disk writes, swap, threads, pipes, sockets - per process group.
- systemd - monitors systemd services using CGROUPS.
- Users and User Groups resource usage - by summarizing the process tree per user and group, reporting: CPU, memory, disk reads, disk writes, swap, threads, pipes, sockets
- logind - collects sessions, users and seats connected.
- Containers - collects resource usage for all kinds of containers, using CGROUPS (systemd-nspawn, lxc, lxd, docker, kubernetes, etc).
- libvirt VMs - collects resource usage for all kinds of VMs, using CGROUPS.
- dockerd - collects docker health metrics.
- Apache and lighttpd -
mod-status(v2.2, v2.4) and cache log statistics, for multiple servers. - IPFS - bandwidth, peers.
- LiteSpeed - reads the litespeed rtreport files to collect metrics.
- Nginx -
stub-status, for multiple servers. - Nginx+ - connects to multiple nginx_plus servers (local or remote) to collect real-time performance metrics.
- PHP-FPM - multiple instances, each reporting connections, requests, performance, etc.
- Tomcat - accesses, threads, free memory, volume, etc.
- web server
access.logfiles - extracting in real-time, web server and proxy performance metrics and applying several health checks, etc. - HTTP check - checks one or more web servers for HTTP status code and returned content.
- HAproxy - bandwidth, sessions, backends, etc.
- Squid - multiple servers, each showing: clients bandwidth and requests, servers bandwidth and requests.
- Traefik - connects to multiple traefik instances (local or remote) to collect API metrics (response status code, response time, average response time and server uptime).
- Varnish - threads, sessions, hits, objects, backends, etc.
- IPVS - collects metrics from the Linux IPVS load balancer.
- CouchDB - reads/writes, request methods, status codes, tasks, replication, per-db, etc.
- MemCached - multiple servers, each showing: bandwidth, connections, items, etc.
- MongoDB - operations, clients, transactions, cursors, connections, asserts, locks, etc.
- MySQL and mariadb - multiple servers, each showing: bandwidth, queries/s, handlers, locks, issues, tmp operations, connections, binlog metrics, threads, innodb metrics, and more.
- PostgreSQL - multiple servers, each showing: per database statistics (connections, tuples read - written - returned, transactions, locks), backend processes, indexes, tables, write ahead, background writer and more.
- Proxy SQL - collects Proxy SQL backend and frontend performance metrics.
- Redis - multiple servers, each showing: operations, hit rate, memory, keys, clients, slaves.
- RethinkDB - connects to multiple rethinkdb servers (local or remote) to collect real-time metrics.
- beanstalkd - global and per tube monitoring.
- RabbitMQ - performance and health metrics.
- ElasticSearch - search and index performance, latency, timings, cluster statistics, threads statistics, etc.
- bind_rndc - parses
named.statsdump file to collect real-time performance metrics. All versions of bind after 9.6 are supported. - dnsdist - performance and health metrics.
- ISC Bind (named) - multiple servers, each showing: clients, requests, queries, updates, failures and several per view metrics. All versions of bind after 9.9.10 are supported.
- NSD - queries, zones, protocols, query types, transfers, etc.
- PowerDNS - queries, answers, cache, latency, etc.
- unbound - performance and resource usage metrics.
- dns_query_time - DNS query time statistics.
- chrony - uses the
chronyccommand to collect chrony statistics (Frequency, Last offset, RMS offset, Residual freq, Root delay, Root dispersion, Skew, System time). - ntpd - connects to multiple ntpd servers (local or remote) to provide statistics of system variables and optional also peer variables.
- Dovecot - POP3/IMAP servers.
- Exim - message queue (emails queued).
- Postfix - message queue (entries, size).
- IPMI - enterprise hardware sensors and events.
- lm-sensors - temperature, voltage, fans, power, humidity, etc.
- Nvidia - collects information for Nvidia GPUs.
- RPi - Raspberry Pi temperature sensors.
- w1sensor - collects data from connected 1-Wire sensors.
- apcupsd - load, charge, battery voltage, temperature, utility metrics, output metrics
- NUT - load, charge, battery voltage, temperature, utility metrics, output metrics
- Linux Power Supply - collects metrics reported by power supply drivers on Linux.
- RetroShare - connects to multiple retroshare servers (local or remote) to collect real-time performance metrics.
- Fail2Ban - monitors the fail2ban log file to check all bans for all active jails.
- FreeRadius - uses the
radclientcommand to provide freeradius statistics (authentication, accounting, proxy-authentication, proxy-accounting).
- opensips - connects to an opensips server (localhost only) to collect real-time performance metrics.
- SMA webbox - connects to multiple remote SMA webboxes to collect real-time performance metrics of the photovoltaic (solar) power generation.
- Fronius - connects to multiple remote Fronius Symo servers to collect real-time performance metrics of the photovoltaic (solar) power generation.
- StiebelEltron - collects the temperatures and other metrics from your Stiebel Eltron heating system using their Internet Service Gateway (ISG web).
- SpigotMC - monitors Spigot Minecraft server ticks per second and number of online players using the Minecraft remote console.
- BOINC - monitors task states for local and remote BOINC client software using the remote GUI RPC interface. Also provides alarms for a handful of error conditions.
- IceCast - collects the number of listeners for active sources.
- Monit - collects metrics about monit targets (filesystems, applications, networks).
- Puppet - connects to multiple Puppet Server and Puppet DB instances (local or remote) to collect real-time status metrics.
You can easily extend Netdata, by writing plugins that collect data from any source, using any computer language.
The Netdata documentation is at https://docs.netdata.cloud. But you can also find it inside the repo, so by just navigating the repo on github you can find all the documentation.
Here is a quick list:
| Directory | Description |
|---|---|
installer |
Instructions to install Netdata on your systems. |
docker |
Instructions to install Netdata using docker. |
daemon |
Information about the Netdata daemon and its configuration. |
collectors |
Information about data collection plugins. |
health |
How Netdata's health monitoring works, how to create your own alarms and how to configure alarm notification methods. |
streaming |
How to build hierarchies of Netdata servers, by streaming metrics between them. |
backends |
Long term archiving of metrics to industry standard time-series databases, like prometheus, graphite, opentsdb. |
web/api |
Learn how to query the Netdata API and the queries it supports. |
web/api/badges |
Learn how to generate badges (SVG images) from live data. |
web/gui/custom |
Learn how to create custom Netdata dashboards. |
web/gui/confluence |
Learn how to create Netdata dashboards on Atlassian's Confluence. |
You can also check all the other directories. Most of them have plenty of documentation.
We welcome contributions. So, feel free to join the team.
To report bugs, or get help, use GitHub Issues.
You can also find Netdata on:
Netdata is GPLv3+.
Netdata re-distributes other open-source tools and libraries. Please check the third party licenses.
Yes.
When people first hear about a new product, they frequently ask if it is any good. A Hacker News user remarked:
Note to self: Starting immediately, all raganwald projects will have a “Is it any good?” section in the readme, and the answer shall be “yes.".
So, we follow the tradition...
These people seem to like it.