This package helps to create DataGrid (CRUD) pages for Laravel 6+ framework applications.
- PHP >=7.1
- Laravel 6+
- Bootstrap 3+
This project is released under the MIT License.
Copyright © 2020 ApPHP.
Begin by pulling in the package through Composer.
composer require apphp/laravel-datagridNext, make sure you connected Bootstrap. You may either pull in the Bootstrap's CSS within your HTML or layout file, or write your own CSS classes based on them.
<link rel="stylesheet" href="//getbootstrap.com/docs/4.0/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css">If you need to modify the datagrid files, you can run:
php artisan vendor:publish --provider="Apphp\DataGrid\DataGridServiceProvider"use Apphp\DataGrid\Pagination;
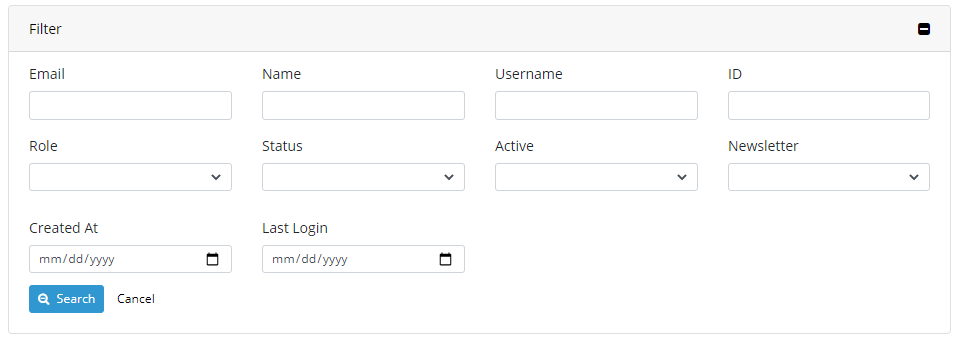
use Apphp\DataGrid\Filter;$filters = [
'act' => ['type' => 'equals', 'value' => 'search'],
'email' => ['title' => 'Email', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%', 'validation' => ['maxLength' => 150]],
'name' => ['title' => 'Name', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%'],
'username' => ['title' => 'Username', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%'],
'user_id' => ['title' => 'ID', 'type' => 'integer', 'compareType' => '=', 'validation' => ['max' => 10000000]],
];Following filter field types are available
| Type | Description |
|---|---|
string |
Any type of strings |
integer or int |
Numeric integer field (HTML type="number" attribute is used) |
set |
Set of values (array) |
date |
The datetime fields |
Each filter field can include following attributes:
| Attribute | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
title |
String | Specifies a title, that will be shown in the label of filter field |
type |
String | Specifies a type of the filter field (see above) |
compareType |
String | Specifies which type of comparison will be used: ex.: '=', '%like%', '!=' etc. |
source |
Array | Specifies the source (array) to 'set' fields |
validation |
Array | Specifies validation rules (array). Possible options: ['minLength'=>2, 'maxLength'=>10, 'min'=>2, 'max'=>100] |
relation |
String | Specifies the relation between 2 models (One-to-One, One-to-Many), ex.: search in posts for users - relation="posts" |
relationXref |
String | Specifies the relation between 2 models (Many-to-Many), ex.: search in roles for users - relation="roles" |
htmlOptions |
Array | Specifies any possible HTML attribute for the field |
disabled |
Boolean | Specifies whether the field is disabled or not (default - not) |
// $query = User::sortable()->orderByDesc('id');
$query = User::orderByDesc('id');
$request = request(); // or get it via function param, like foo(Request $request){...}
$url = route('backend.users.submitRote');
$cancelUrl = $url;
$filters = [];
$filter = Filter::init($query, $request, $filters, $url, $cancelUrl, 'collapsed');
$filter = $filter::filter();
$filterFields = $filter::getFilterFields();
$query = $filter::getQuery();$sort = $request->get('sort');
$direction = $request->get('direction');$pagination = Pagination::init($query, 20, $sort, $direction, $filterFields)::paginate();
$paginationFields = $pagination::getPaginationFields();
$users = $pagination::getRecords();return view('backend.users.mainView', compact('users', 'filterFields', 'paginationFields'));<script>
{!! \Apphp\DataGrid\Filter::renderJs() !!}
</script>
@if(count($records))
{!! \Apphp\DataGrid\Filter::renderFields() !!}
<!-- YOUR TABLE WITH RECORDS DATA -->
@foreach ($records as $record)
<!-- ... -->
@endforeach
<!-- YOUR TABLE WITH RECORDS DATA -->
{!! \Apphp\DataGrid\Pagination::renderLinks() !!}
@else
{!! \Apphp\DataGrid\Message::warning('Sorry, no records were found. Please adjust your search criteria and try again.') !!}
@endifTo change default settings and enable some extra features you can export the config file:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-datagrid:configTo change or add new translation files you can export the language files:
php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-datagrid:langTo change HTML template of the datagrid or use your own, publish view file and customize it to suit your needs.
$ php artisan vendor:publish --tag=laravel-datagrid:viewsNow you should have a datagrid.php file in the config folder of your application. If you need to force to re-publish the config file to use --force.
To rum unit testing simply do following:
./vendor/bin/phpunit vendor\\apphp\\laravel-datagrid\\tests\\TestDataGridMessage.phpor your may add additional section to your composer.json file:
"scripts": {
"tests": "phpunit --colors=always",
"test": "phpunit --colors=always --filter",
}and then rum unit following command:
composer tests vendor\\apphp\\laravel-datagrid\\tests\\TestDataGridMessage.php
composer tests vendor\\apphp\\laravel-datagrid\\tests\\TestDataGridPagination.php
composer tests vendor\\apphp\\laravel-datagrid\\tests\\TestDataGridFilter.phpand so on...
public function index(Request $request)
{
// Additional data
$roles = Role::rolesList();
$statuses = User::statusesList();
$actives = [0 => 'Not Active', 1 => 'Active'];
// Define filters and filter field types
$filters = [
'act' => ['type' => 'equals', 'value' => 'search'],
'email' => ['title' => 'Email', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%', 'validation' => ['maxLength' => 150]],
'name' => ['title' => 'Name', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%'],
'username' => ['title' => 'Username', 'type' => 'string', 'compareType' => '%like%'],
'user_id' => ['title' => 'ID', 'type' => 'integer', 'compareType' => '=', 'validation' => ['max' => 10000000]],
'role' => ['title' => 'Role', 'type' => 'user_role', 'compareType' => '', 'source' => $roles],
'status' => ['title' => 'Status', 'type' => 'user_status', 'compareType' => '', 'source' => $statuses],
'active' => ['title' => 'Active', 'type' => 'user_active', 'compareType' => '', 'source' => $actives],
'created_at' => ['title' => 'Created At', 'type' => 'date', 'compareType' => 'like%'],
'last_logged_at' => ['title' => 'Last Login', 'type' => 'date', 'compareType' => 'like%'],
];
$query = User::orderByDesc('id');
// Handle filters and prepare SQL query
$filter = Filter::init($query, $request, $filters, route('users.list'), route('users.list'), 'collapsed');
$filter = $filter::filter();
$filterFields = $filter::getFilterFields();
$query = $filter::getQuery();
// Sorting
$sort = $request->get('sort');
$direction = $request->get('direction');
// Pagination
$pagination = Pagination::init($query, 20, $sort, $direction, $filterFields)::paginate();
$paginationFields = $pagination::getPaginationFields();
$users = $pagination::getRecords();
return view('users.list', compact('users', 'filterFields', 'paginationFields'));
}If you use some kind of packages for column sorting, like kyslik/column-sortable, you have to change usage of Model to following:
Without sorting
$query = User::orderByDesc('id');With column sorting
$query = User::sortable()->orderByDesc('id');You have 2 way to render table content. The first is to write creating table manually in view file. Look on example below:
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-bordered table-striped">
<thead>
<tr>
<th class="text-right" width="60px">@sortablelink('user_id', 'ID')</th>
...
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach ($users as $user)
<tr>
<td class="text-right">{{ $user->user_id }}</td>
...
</tr>
@endforeach
</tbody>
</table>
</div>The second way is to use GridView helper. Look on example below:
// GridView - initialized in Controller
$gridView = GridView::init($records);
return view('backend.users', compact(..., 'gridView'));{{-- Render table content --}}
{!!
$gridView::renderTable([
'user_id' => ['title' => 'ID', 'width'=>'60px', 'headClass'=>'text-right', 'class'=>'text-right', 'sortable'=>true, 'callback'=>null],
'username' => ['title' => 'Username', 'width'=>'', 'headClass'=>'text-left', 'class'=>'', 'sortable'=>true],
'name' => ['title' => 'Name', 'width'=>'', 'headClass'=>'text-left', 'class'=>'', 'sortable'=>true],
'email' => ['title' => 'Email', 'width'=>'', 'headClass'=>'text-left', 'class'=>'text-truncate px-2', 'sortable'=>true],
'created_at' => ['title' => 'Created At', 'width'=>'160px', 'headClass'=>'text-center', 'class'=>'text-center px-1', 'sortable'=>true],
'last_login_at' => ['title' => 'Last Login', 'width'=>'160px', 'headClass'=>'text-center', 'class'=>'text-center px-1', 'sortable'=>false],
])
!!}You may also use a callback attribute to customize values of the specific field. This attribute accepts a function, link to function or a closure.
Below you may find few examples to get a feel:
Show specific badge if user has verified
'callback'=>function($user){ return $user->isVerified() ? '<span class="badge badge-primary">Verified</span>' : '<span class="badge badge-secondary">Waiting</span>'; }Show a list of user roles, get array of roles via $roles parameter
'callback'=>function($user) use ($roles){ $output = ''; if(!count($user->roles)) $output .= '<span class="badge badge-light">User</span>'; foreach($user->roles as $role) { $output .= '<span class="badge badge-info">'.$roles[$role->name].'</span> '; } return $output; }Show user's avatar with a link to edit
'callback'=>function($user){ return '<img src="'.$user->avatar.'" alt="avatar" /> <a href="'.route('users.show', $user).'" title="Click to edit">'.$user->username.'</a>'; }