EnvOne is a zero-dependency module that loads dynamic environment configurations from a .env.config file, and process it as environment variables into process.env - Relief from messing with your environments!
# install with npm
npm install envone
# or install with Yarn
yarn add envoneAs early as possible in your application, require and configure envone.
require('envone').config()Create a .env.config file in the root directory of your project. Add environment-specific configurations as JSON format. For example:
{
"SERVER_URL": "https://test-{{ENV}}.application.abcd.com",
"CONTACT_US_EMAIL": {
"DEV": "hello-dev@abcd.com",
"STAG": "hello-stag@abcd.com",
"PROD": "hello@abcd.com"
},
}Now, create your .env file only with ENV=DEV or pass it when you start your application..!
ENV=DEV node index.jsNow, process.env has the keys and values you defined in your .env.config file. Here, process.env.CONTACT_US_EMAIL will have the value for DEV key as the application is started with ENV=DEV.
function request(serverUrl) {
// send backed request
// serverUrl = https://test-DEV.application.abcd.com
}
const res = request(process.env.BFF_URL)
function setContactUseEmail(emailAddress) {
// send email
// emailAddress = hello-dev@abcd.com
}
const emailRes = request(process.env.CONTACT_US_EMAIL)Returns user defined environment variable keys as an array (based on .env.config).
const envOne = require('envone');
envOne.config();
...
const envKeys = envOne.getUserEnvironmentKeys();
// envKeys = ['BFF_URL', 'DB_PASSWORD']Check here for how to use this : EnvOne- Example Node.js Server
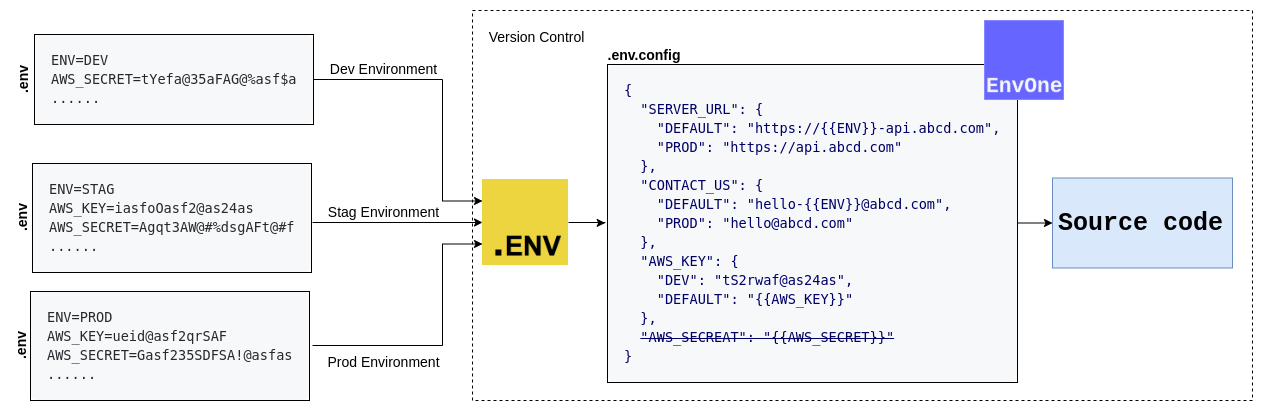
Dynamic environment configurations will be loaded from .env.config file, and will be replaced based on given environment variables.
.env.configshould be a JSON configurations (key and values pairs)- Value for each key can be string or object based on the application environment.
key: string value: Value should be plain string, and dynamic part should be wrapped with{{and}}. For example, If you dynamically change thebase_urlin yourserver_url(You should pass thebase_urlwhen you start your application as environment variable.),
{ "server_url": "{{base_url}}/api/v1" }key: object: Value should be JSON object, and each keys should be based on environments(e.g:DEV,STAG,PROD). This environment-key will be picked from the environment variables such asENVorNODE_ENV.
{ "ACCESS_KEY": { "DEV": "w5Dty3EaFi983ew", "STAG": "u7Awda72Sd2Wfaf", "PROD": "p9AfawaCa23AwrG" } } - Use the
DEFAULTto defined your environment variables that have the same patterns across the environments. For example,Here,CONTACT_US_EMAIL (DEV): hello-dev@abcd.com CONTACT_US_EMAIL (STAG): hello-stag@abcd.com CONTACT_US_EMAIL (PROD): hello@abcd.comDEVandSTAGenvironment variables have the same pattern, andPRODdiffered from that pattern. So you can simply define,{ "CONTACT_US_EMAIL": { "DEFAULT": "hello-{{ENV}}@abcd.com", "PROD": "hello@abcd.com" } } - Here, you have the flexible to override any environment variables through the direct environment variables. You can simply pass that variable during the application startup to override any values. For example:
You can use the following command to start the applications,
{ "SERVER_URL": "{{BASE_URL}}/api/v1", "ACCESS_KEY": { "DEV": "w5Dty3EaFi983ew", "STAG": "u7Awda72Sd2Wfaf", "PROD": "p9AfawaCa23AwrG" }, }Here, the configuration inSERVER_URL=https://test.abc.com/rest ACCESS_KEY=pWs13dSwerF node index.js
.env.configwill be ignored, andSERVER_URLandACCESS_KEYwill be picked from the startup environment variables. - Define your secret environment variables with
isSecretfield.This will help you to get all the secret environment keys as an array from the envOne config output,{ "DB_PASSWORD": { "DEV": "w5Dty3EaFi983ew", "DEFAULT": "{{DB_PASSWORD}}", "isSecret": true, }, "AWS_SECRET": { "DEV": "asfSAF@afawr21FA", "DEFAULT": "{{AWS_SECRET}}", "isSecret": true, } }const envData = require('envone').config(); // Output => envData.SECRET_ENVIRONMENT_KEYS = ["DB_PASSWORD", "AWS_SECRET"]
- Add
isRequiredattribute to indicate the required environment keys. EnvOne prevents from starting the server without these required environment keys.{ "AWS_SECRET": { "DEV": "asfSAF@afawr21FA", "DEFAULT": "{{AWS_SECRET}}", "isSecret": true, "isRequired" : true } }
Default: path.resolve(process.cwd(), '.env.config')
You can specify a custom path of .env.config, if that file is located elsewhere from default root path.
require('envone').config({ path: '/custom-path/.env.config' })Default: false
You can turn on logging to help debug the environment related issues (why certain keys or values are not being set as you expect)
require('envone').config({ debug: true })-
Is it hard to handle your non-secret environment variables across your environments?
CONTACT_US_EMAIL (DEV): hello-dev@abcd.com CONTACT_US_EMAIL (STAG): hello-stag@abcd.com CONTACT_US_EMAIL (PROD): hello@abcd.com -
Are you suffering to manage a lot of environment variables across your environments?
-
Do you follow any unique patterns across your environments?
DEV: https://test-dev.application.abcd.com STAG: https://test-stag.application.abcd.com PROD: https://test-prod.application.abcd.com -
Manage your required environment keys and secret environments keys easily.
-
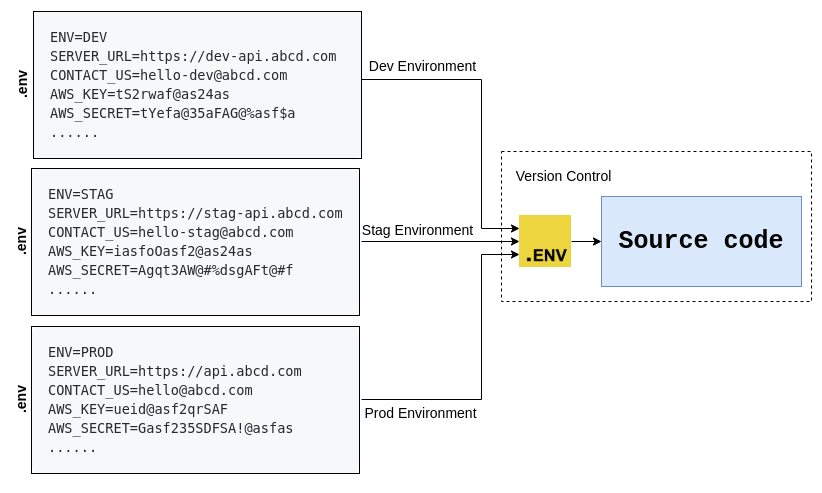
Where do you keep your environment variables across your environments? You can commit .env.config to your version control to reduce your management of non-secret environment variables.
Dotenv helps to load the environment variables from .env file from your root directory to process.env. Here,
- You can't commit
.envfile to your source control as it might have secrets. - It might be hard to manage different environment files across different environments.
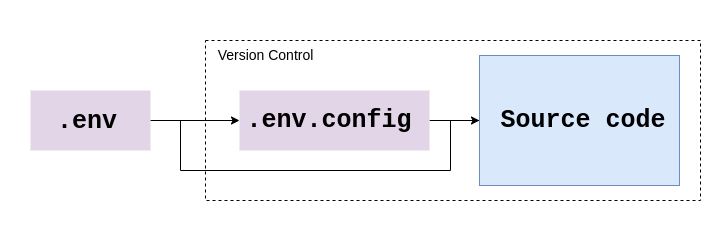
EnvOne helps you to migrate the non-secret environment variables from .env to .env.config.
- You can commit
.env.configfile to your source control as it doesn't have any secrets. - You don't have to manage multiple files, you can keep one
.env.configfor all of your environments. - You can easily remove
EnvOnefrom your eco-system and pass the Env variables directly to the application. (As EnvOne also loads Env variables toprocess.env) - Keep your environment variables clean and manageable across multiple environments.
.env.configalso might depend on some Env variables to replace the dynamic configurations. (You can use dotenv or you can directly pass those with application startup command)
You can add any suggestions/feature requirements/bugs to the Github issues page : https://github.com/apisquare/envone/issues
Add your fixes and development changes as pull requests to this repository.