r53spflatis an extension to sender-policy-flattener which is a different project maintaind by centanu.r53spflatcan update the SPF TXT records in Amazon Route53r53spflatwas adapted fromcfspflat- which provides the same capability for Cloudflare DNS
Sender Policy Framework (SPF) has certain restricitions on the number of DNS lookups (10) to validate a sender is authorized by SPF.
- Organizations utilizing vendors and SaaS products that send email on their behalf. They do this by adding an
includefor an SPF record the vendor provides - and manages. - The vendor managed SPF record contains the
ip4andip6records for that vendors email infrastrucure and often contains additionalincludestatements. - As each vendor SPF record is included to your SPF it requires more DNS lookups. This can exceed the SPF protocol limit of 10 lookups. When this happens, your email can be rejected by recipients because the authorized sender's IP was never reached.
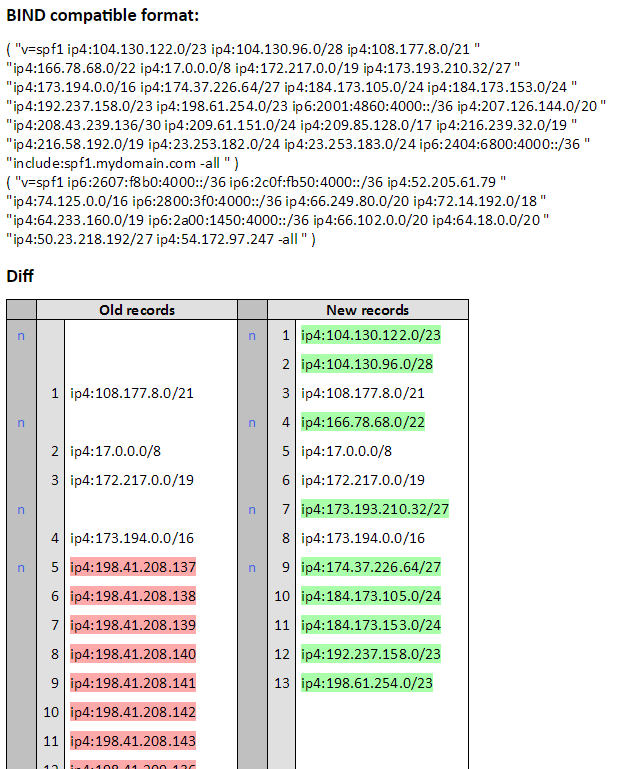
- SPF Flattening is the process of resolving the authorized senders SPF
includerecords intoip4andip6records to reduce the number of DNS lookups. - Converting the
includerecords toip4andip6statements can be a problem if the vendor modifies their SPF record. How do you keep them in sync?- sender-policy-flattener detects these changes and reports them by email.
r53spflatusessender-policy-flattener, but includes an--updatecapability.
Quick overview:
% r53spflat -h
usage: r53spflat [-h] [-c CONFIG] [-o OUTPUT] [--update-records] [--force-update]
[--no-email]
A script that crawls and compacts SPF records into IP networks. This helps to
avoid exceeding the DNS lookup limit of the Sender Policy Framework (SPF)
https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc7208#section-4.6.4
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-c CONFIG, --config CONFIG
Name/path of JSON configuration file (default:
spfs.json)
-o OUTPUT, --output OUTPUT
Name/path of output file (default spf_sums.json)
--update-records Update SPF records in Route53
--force-update Force an update of SPF records in Route53
--no-email don't send the email- The
sender-policy-flattenerpython module is installed as part ofr53spflat - The existing core of
spflatis kept mostly intact, so the basic features are maintained byr53spflat. - The changes to accomodate
r53spflatwere in the parameter handling and adding the Route53 updates to the processing look. - The
boto3library, with some abstraction classes, is used to make the zone updates in Route53. r53spflateliminates many of the command arguments of spflat in favor of using the json config file.- Rotue53 TXT records are automatically generated and updated when the configuration changes.
- With
r53spflatyou can completely automate your SPF flattening using cfspflat with the--updateswitch in a cron job, even silently with the--no-emailswitch
% pip install r53spflat- But it's advisable to do this in its own venv:
% python3 -m venv spfenv
% source spfenv/bin/activate
% pip install r53spflat- pip will install the prerequisites, including the
sender-policy-flattner(spflat),dnspython,netaddr, andboto3python modules. - The executable is installed in bin of the venv as
r53spflat
Create the TXT SPF record on zone apex used (e.g. example.com), At the end of this anchor record include the first SPF record that slpat will write - spf0.example.com
- we also include our own
ip4andip6entries in this anchor record.
example.com TXT "v=spf1 mx include:spf0.example.com -all"
- This anchor record is never changed by
r53spflat. It's purpose is to link to the first SPF record in the chain thatr53spflatmanages.
Create a spfs.json file. Add all the entries required:
r53spflatuses the same configuration and sums file formats as the originalspflat.- If you already use spflat you can use those files as is with r53spflat.
- There is one extension - the "update_subject" entry containing the subject of the email sent when r53spflat has updated your SPF records. This message will contain the same detail spflat provides.
spfs.jsonis the default name of the config file, but it can be specified with the--configswitch.- Here is an example config file:
{
"sending domains": {
"example.edu": {
"amazonses.com": "txt",
"goodwebsolutions.net": "txt",
.... more sender spf's here ....
"delivery.xyz.com": "txt",
"spf.protection.outlook.com": "txt"
}
},
"resolvers": [
"1.1.1.1", "8.8.8.8"
],
"email": {
"to": "dnsadmins@example.com",
"from": "spf_monitor@example.com",
"subject": "[WARNING] SPF Records for {zone} have changed and should be updated.",
"update_subject" : "[NOTICE] SPF Records for {zone} have been updated.",
"server": "smtp.example.com"
},
"output": "monitor_sums.json"
}- The
sending domainssection is required and contains sending domain entries: this is your sender domain (e.g. example.com for j.smith@example.com, noreply.example.com for deals@noreply.example.com ) There can be multiple sending domains in the config file. - Each sending domain contains dns spf records for the dns
includerecords of your approved senders.These dns names are resolved and flattened:- These entries are in the key-value pairs of : .
- Record type can be "txt" (other SPF records), "A" and "AAAA" records (for specific hosts).
- The
resolverssection is optional (using the system default DNS resolvers if none are supplied) - The
emailstanza is required and is global (i.e. for allsending domains). This section includes:subject(optional) is the email subject if a change was detected but no updates were made. The default message is the one shown in the example.update_subject(optional) is the email subject if a change was detected and the dns records were updated. The default message is shown in the example.to- is required - this is the destination for emails sent byr53spflatfrom- is required - the source email of the messagesr53spflatsendsserver- is required - your mail relay.
outputis the file that maintains the existing state and checksum of sender records. If this is not specifiedspfs_sum.jsonis used.
- The
outputfile is a JSON file only updated if it is new (empty) or the records have been updated. - Likewise the default output file is
spf_sums.jsonbut can be changed in the config file or by the--outputswitch. - This contains the list of flattened spf records and a checksum used to assess changes in senders records.
- Because you recieve emails of detected changes or updates, there is little reason to care about the output file.
- The AWS user or role used for
r53spflatmust have these permissions to make updates:route53:ListHostedZonesto Route53route53:ChangeResourceRecordSetsandroute53:ListResourceRecordSetsto the zones that will be updated
- If
r53spflatrun on an AWS EC2 instance, an IAM role with the required privileges can be attached to the instance. - If
r53spflatruns on prem, API keys are required to make the AWS Route53 updates and placed in a configuation file.- Configuring this beyond our scope: refere to AWS cli
- Route53 is a global service, so any region can be specified.
- These credentials are typically in
~/.aws/credentialsand~/.aws/config
- It's also possible to pass the credentials as environment variables.
- Run r53spflat twice:
% r53spflat --no-email
% r53spflat --force - The first time constructs the base records and the second time forces the dns updates.
- With force update the DNS records are created even if a change hasn't been detected.
- A list of the records will be sent to your email.
- You are up and running:
- You can run
r53spflatin advisory mode (likespflat) sending you emails notifying of changes - Or you can run it with the
--update-recordsswitch and update your records automatically whenever they change (still giving you notifications of the changes made.)
- You can run
- Example from
sender-policy-flattenerREADME - This would be in