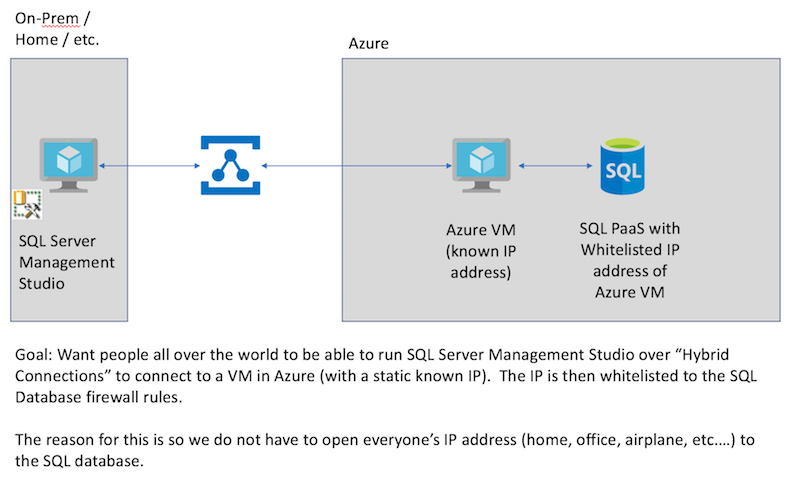
Using Azure Relay for allowing access to SQL PaaS (and CosmosDB, and anything you want) without a VPN or without whitelisting your IP address in SQL Firewall.
Customers have asked for a way where they can connect to SQL PaaS, but do not want to whitelist all their developers machines IP addresses. This is important since developers work from homes, airplanes, hotspots, etc. The goal is to allow the developer to securly connect to SQL PaaS without whitelisting their IP. This technique is not just limited to Azure SQL Database (just about any resource can be enabled).
I saw a feature about Hybrid Connections that I through would be great, but it is very much tied to Azure App Services. See: https://azure.microsoft.com/en-us/resources/videos/azure-app-service-with-hybrid-connections-to-on-premises-resources/
I talked with Clemens, who was working on a more generic solution he was working on building. https://github.com/clemensv/azure-relay-bridge (This might move to the Azure repository in the future)
While the below diagram is my original goal, it turns out Azure Relay passes my client machine's IP address to SQL Database. This defeats the point of the relay (from a firewall rule persepective). But, we are in luck, since we can just allow the VNET the receiver machine is on, access to SQL Database and we can connect.
-
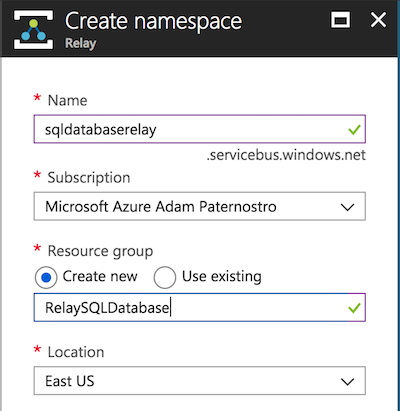
Azure Relay
-
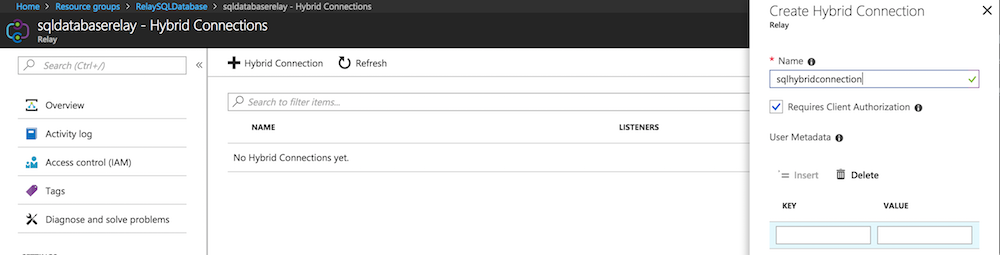
In the newly created relay click on "Hybrid Connections"
-
Click on the Hybrid Connection.
-
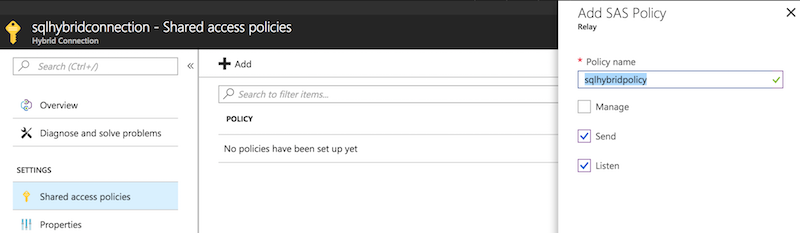
Click on the policy and copy the Primary Connection String
- e.g. Endpoint=sb://sqldatabaserelay.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=sqlhybridpolicy;SharedAccessKey={REMOVED};EntityPath=sqlhybridconnection
-
Create an Azure VM (aka "Reciever")
- I created a Windows Server 2016 VM
- The name is not important.
- The region should be in the same region as your database.
- The machine must be on the VNET you want to trust to your SQL Database. My VNET is named: aRelayDest-VNET
- Login into the VM (turn off IE enhanced security).
- Download the MSI from here: https://github.com/clemensv/azure-relay-bridge/releases
- Install the software.
-
Now create a SQL Database in Azure
- You can use an existing one or create a new one.
- If you using an existing database, the important step here is to set the firewall rules.
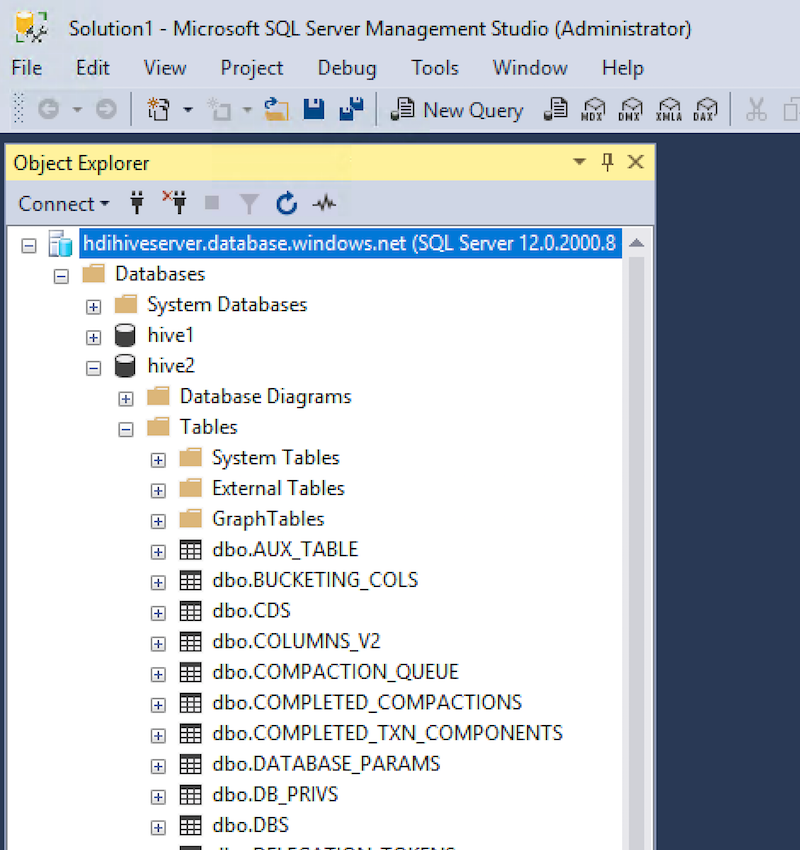
- My database server is: hdihiveserver.database.windows.net
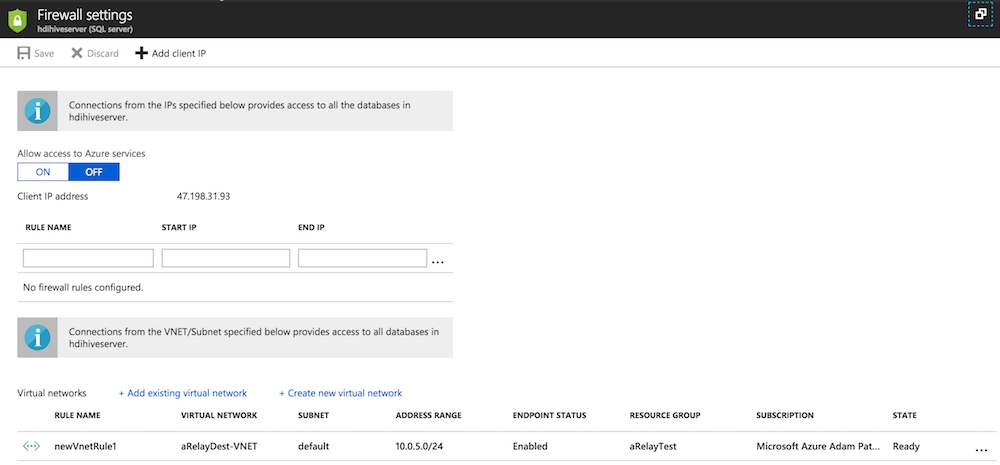
- Click on the Firewall rules and set the following
- Allow Access to Azure Services: You can choose On or Off (I did Off since I just want my VNET to access)
- Client IP Addresses: I left blank since I am trusting my VNET.
- Click "Add existing virtual network". Select the Virtual Network your Receiver VM is on
-
Client machine (Install)
- You now need to configure your machine (or any other client)
- Download the MSI from here: https://github.com/clemensv/azure-relay-bridge/releases
- Install the software.
-
Client machine (Configure hosts file)
-
Open a cmd prompt (as administrator)
-
Open Notepad
-
Open C:\Windows\System32\drivers\etc\hosts
-
Add this entry (your database name): 127.0.5.1 hdihiveserver.database.windows.net
-
Save the hosts file
-
Please read https://github.com/clemensv/azure-relay-bridge about selecting an IP address.
-
Client
cd "C:\Program Files\Azure Relay Bridge"
azbridge -L 127.0.5.1:1433:sqlhybridconnection -x Endpoint=sb://sqldatabaserelay.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=sqlhybridpolicy;SharedAccessKey={REMOVED};EntityPath=sqlhybridconnection
Generic:
azbridge -L 127.0.5.1:1433:{hybrid-connection-name} -x {SAS-Token}
Receiver
cd "C:\Program Files\Azure Relay Bridge"
azbridge -R sqlhybridconnection:hdihiveserver.database.windows.net:1433 -x Endpoint=sb://sqldatabaserelay.servicebus.windows.net/;SharedAccessKeyName=sqlhybridpolicy;SharedAccessKey={REMOVED};EntityPath=sqlhybridconnection
Generic:
azbridge -R {hybrid-connection-name}:{sql-server-name}.database.windows.net:1433 -x {SAS-Token}
Run SQL Server Management Studio and connect to your SQL Server "as normal", but without whitelisting your IP address.