A Vapor integration for PayPal's REST API. Mostly incomplete, but good for basic payments
Add the package to your manifest's dependencies and to any targets you want access to the package in:
.package(url: "https://github.com/skelpo/PayPal.git", from: "0.1.0")Run vapor update or swift package update and regenerate your Xcode project if you are developing with Xcode.
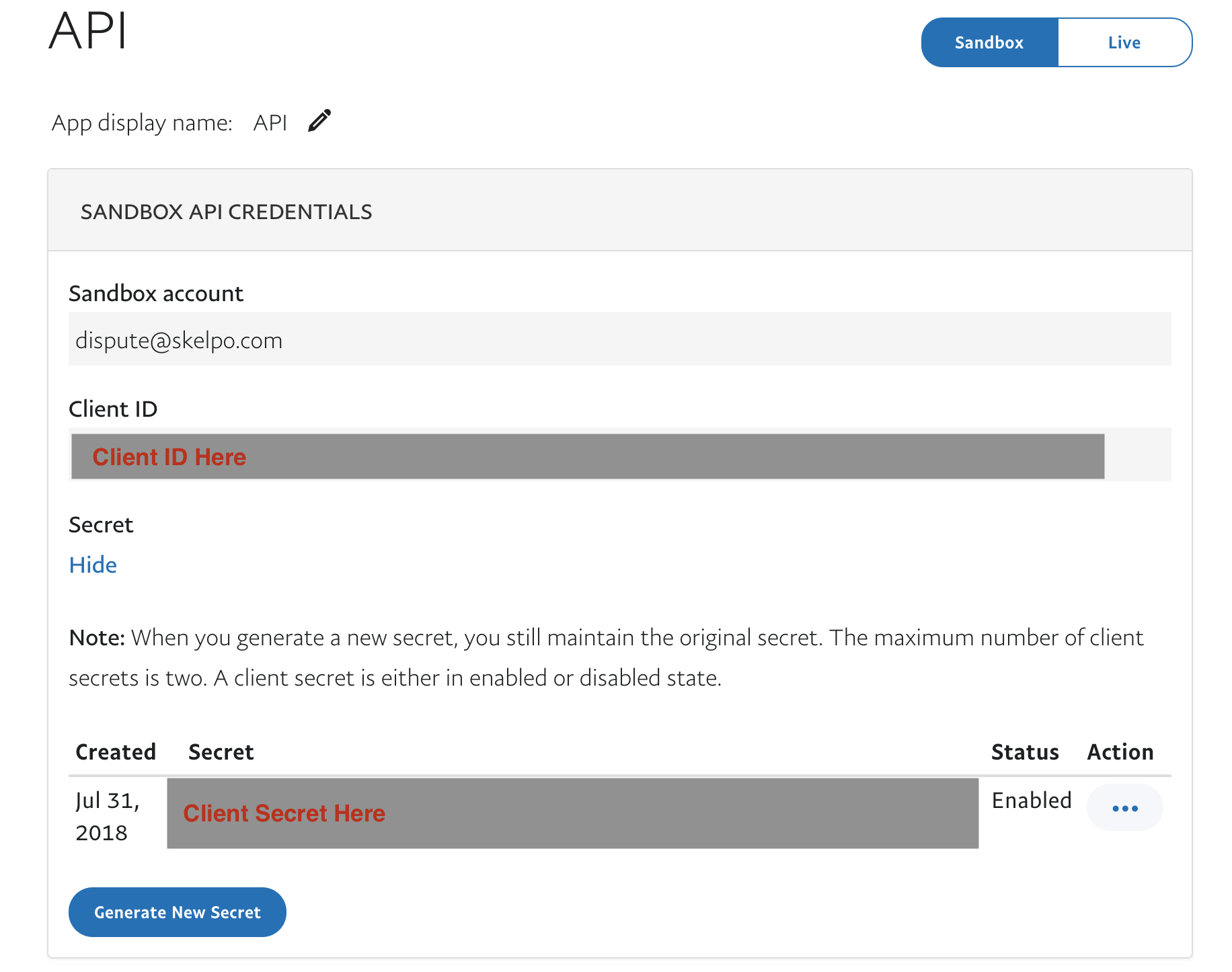
The PayPal package uses two environment variables to authenticate your app with PayPal, PAYAPL_CLIENT_ID and PAYPAL_CLIENT_SECRET. You can access these keys by going to your developer dashboard and selecting the app you want to use the package for:
You can then set these keys in Xcode's environment variables or in the command-line with export <KEY-NAME>=<KEY-VALUE>.
Note: If you set the keys in Xcode, they will need to be re-added every time you regenerate the project. If you set the keys in the command-line, you will need to close Xcode and regenerate your project.
You can log request/response pairs that result in an API error if you are in debug mode and set the env var PAYPAL_LOG_API_ERROR to TRUE.
In your configure.swift file, you will need to import the PayPal module and register the PayPalProvider with your app's services:
try services.register(PayPalProvider())To create and execute a payment, start by creating a Payment object to send to PayPal:
let address = try Address(
recipientName: "Ira Harding",
defaultAddress: true,
line1: "578 Wild Wood",
line2: nil,
city: "New Haven",
state: "CN",
countryCode: "US",
postalCode: "79812",
phone: nil,
type: nil
)
let item = try Payment.Item(
quantity: "3",
price: "39.00",
currency: .usd,
sku: "8EFAFEF3-72D2-4E5C-85EC-C14BA2F9D997",
name: "Plum Pudding",
description: "With sugar an inch thick",
tax: "8.00"
)
let details = try DetailedAmount.Detail(
subtotal: "117.00",
shipping: "15.00",
tax: "8.00",
handlingFee: "10.00",
shippingDiscount: nil,
insurance: nil,
giftWrap: nil
)
let amount = try DetailedAmount(currency: .usd, total: "150.00", details: details)
let items = try Payment.ItemList(
items: [item],
address: nil,
phoneNumber: nil
)
let transaction = try Payment.Transaction(
amount: amount,
payee: Payee(email: "payee@example.com", merchant: nil, metadata: nil),
description: nil,
payeeNote: "Thanks for paying for the order!",
custom: nil,
invoice: nil,
softDescriptor: nil,
payment: .unrestricted,
itemList: items,
notify: "https://example.com/notify"
)
let payment = try Payment(
intent: .sale,
payer: PaymentPayer(method: .paypal, funding: nil, info: nil),
context: nil,
transactions: [transaction],
experience: nil,
payerNote: "Thanks for ordering!",
redirects: Redirects(return: "https://example.com/approved", cancel: "https://example.com/canceled")
)Then get the registered Payments service from the container you have access to. This will be a Request object if you are in a route handler:
let payments = try request.make(Payments.self)You can then create the payment with PayPal:
let payment = try payments.create(payment: payment)This method returns a future with the payment that was created. In the payment is an array of URIs that are related to the payment you just created. One of them is for letting the buyer authorize the payment, called approval_url. You send this as a redirect response back to the client:
return payment.map { payment -> Response in
guard let uri = result.links?.filter({ $0.rel == "approval_url" }).first?.href else {
throw Abort(.failedDependency, reason: "Cannot get payment approval URL")
}
return req.redirect(to: uri)
}When this response is sent to the client, they will be redirected to the payment approval page on PayPal. Depending on what they do then, they will be redirected to one of the links that was registered with the payment (https://example.com/approved or https://example.com/canceled in our case). These should be URIs for routes in your app.
If the payment is approved by the buyer, they will be redirected back to your 'approved' route. Here you can get the payment ID and the payer ID from the URI's query-strings and execute the payment:
func approved(_ request: Request)throws -> Future<SOME-TYPE> {
let paymentID = try request.query.get(String.self, at: "paymentId")
let payerID = try request.query.get(String.self, at: "PayerID")
let payments = try request.make(Payments.self)
let executor = try Payment.Executor(payer: payerID, amounts: [ DetailedAmount(currency: .usd, total: "150.00", details: nil) ])
payments.execute(payment: paymentID, with: executor)
}Make sure the amount in the executor object is the proper currency and equals the amount of the payment you created.