Serializable map of integers to bytes with near zero parsing.
from mapbuffer import MapBuffer, IntMap
data = { 2848: b'abc', 12939: b'123' }
mb = MapBuffer(data)
with open("data.mb", "wb") as f:
f.write(mb.tobytes())
with open("data.mb", "rb") as f:
binary = f.read()
# Uses mmap to read the file.
# Cannot access data after file is closed.
with open("data.mb", "rb") as f:
mb = MapBuffer(f)
mb = MapBuffer(binary)
print(mb[2848]) # fast: almost zero parsing required
>>> b'abc'
# assume data are a set of gzipped utf8 encoded strings
mb = MapBuffer(binary,
compress="gzip",
frombytesfn=lambda x: x.decode("utf8")
)
print(mb[2848])
>>> "abc" # bytes were automatically decoded
# There is also an IntMap class for u64 -> u64 mapping
# You don't need to specify compress or from/to bytes
# The serialization is also smaller as it's only the
# index, no payload. Everything else is the same.
im = IntMap({ 1: 2, 3: 4 })
print(im[1]) # 2
with open("data.im", "wb") as f:
f.write(im.tobytes())pip install mapbufferMapBuffer is designed to allow you to store dictionaries mapping integers to binary buffers in a serialized format and then read that back in and use it without requiring an expensive parse of the entire dictionary. Instead, if you have a dictionary containing thousands of keys, but only need a few items from it you can extract them rapidly.
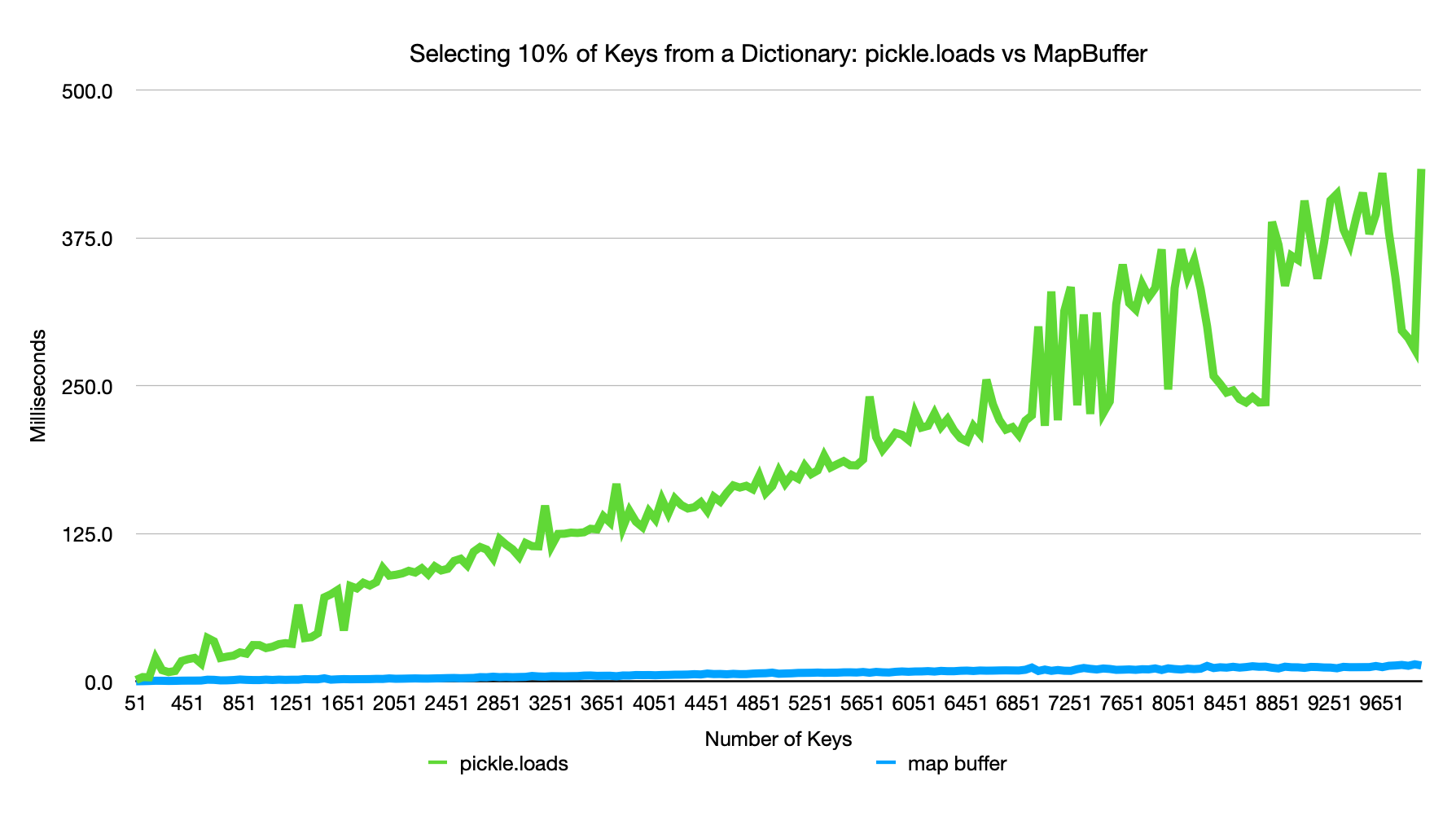
This serialization format was designed to solve a performance problem with our pipeline for merging skeleton fragments from a large dense image segmentation. The 3D image was carved up into a grid and each gridpoint generated potentially thousands of skeletons which were written into a single pickle file. Since an individual segmentation could cross many gridpoints, fusion across many files is required, but each file contains many irrelevant skeleton fragments for a given operation. In one measurement, pickle.loads was taking 68% of the processing time for an operation that was taking two weeks to run on hundreds of cores.
Therefore, this method was developed to skip parsing the dictionaries and rapidly extract skeleton fragments.
The MapBuffer object is designed to translate dictionaries into a serialized byte buffer and extract objects directly from it by consulting an index. The index consists of a series of key-value pairs where the values are indices into the byte stream where each object's data stream starts.
This means that the format is best regarded as immutable once written. It can be easily converted into a standard dictionary at will. The main purpose is for reading just a few objects out of a larger stream of data.
The following benchmark was derived from running perf.py.
The byte string format consists of a 16 byte header, an index, and a series of (possibily individually compressed) serialized objects.
HEADER|INDEX|DATA_REGION
| Format Version | description |
|---|---|
| 0 | Initial Release |
| 1 | Adds crc32c check values to each item. |
b'mapbufr' (7b)|FORMAT_VERSION (uint8)|COMPRESSION_TYPE (4b)|INDEX_SIZE (uint32)
Valid compression types: b'none', b'gzip', b'00br', b'zstd', b'lzma'
Example: b'mapbufr\x00gzip\x00\x00\x04\x00' meaning version 0 format, gzip compressed, 1024 keys.
<uint64*>[ label, offset, label, offset, label, offset, ... ]
The index is an array of label and offset pairs (both uint64) that tell you where in the byte stream to start reading. The read length can be determined by referencing the next offset which are guaranteed to be in ascending order. The labels however, are written in Eyztinger order to enable cache-aware binary search.
The index can be consulted by conducting an Eytzinger binary search over the labels to find the correct offset.
The data objects are serialized to bytes and compressed individually if the header indicates they should be. They are then concatenated in the same order the index specifies. The last four bytes are a crc32c check value that was added in format version 1.
The concept here was inspired by Flatbuffers.Flexbuffers, however the Python implementation (not the C++ implementation) there was a little slow as of this writing. We also add a few differences:
- Eytzinger ordering of labels to potentially achieve even higher read speeds
- Structure optimized for network range reads.
- Integer keys only.
- Compression is built in to the structure.
- Interface has a lot of syntatic sugar to simulate dictionaries.