GraphiQL middleware for ASP.NET Core with JWT-bearer token retireval built in. Forked from https://github.com/JosephWoodward/graphiql-dotnet. Either you can paste in a bearer token received from your auth, or you can pass user credentials to your authorization mutation. This fork does not handle the authorization process in GraphQl or your API.
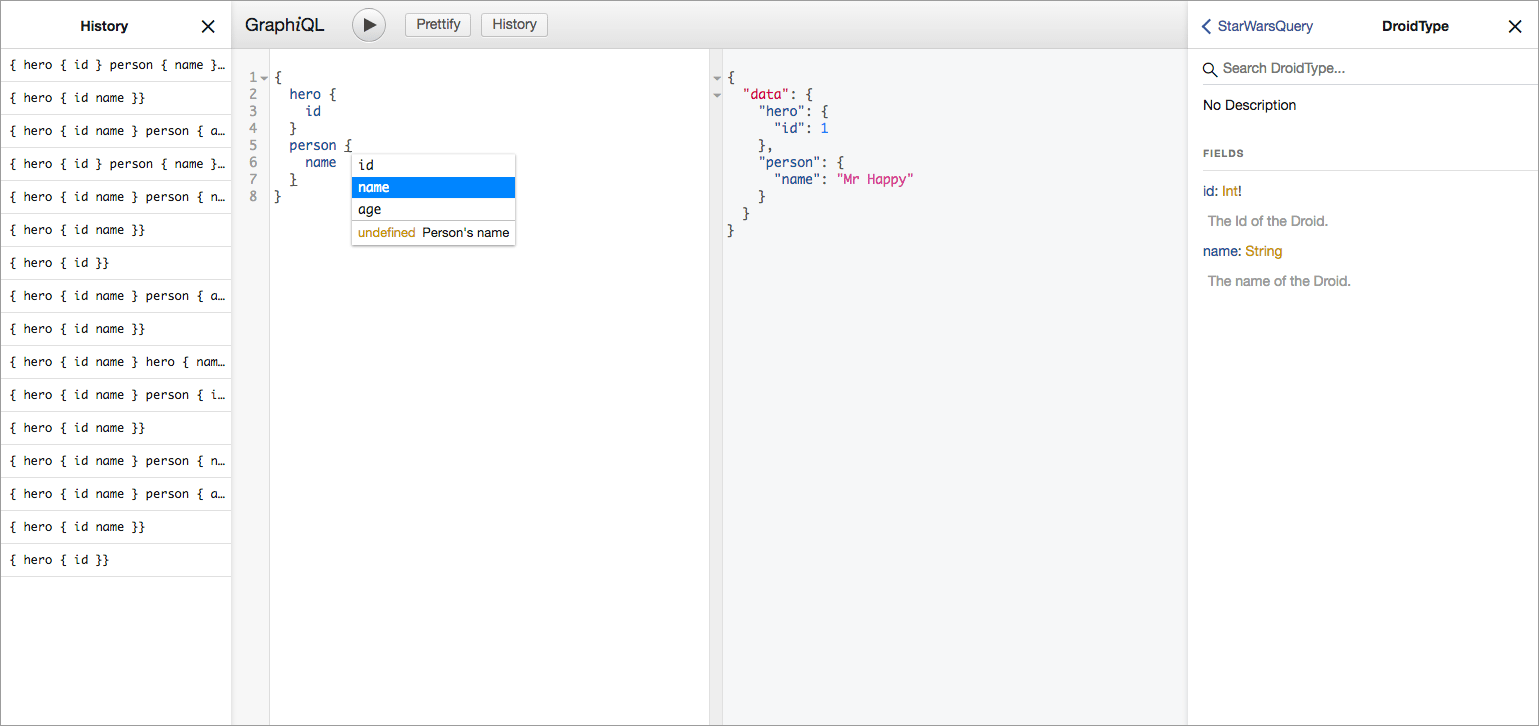
GraphiQL an in-browser IDE for exploring GraphQL (see here). Normally in order to set GraphiQL up you need to do so via Node.
GraphiQL features include:
- Syntax highlighting.
- Intelligent type ahead of fields, arguments, types, and more.
- Real-time error highlighting and reporting.
- Automatic query completion.
- Run and inspect query results.
GraphiQL.NET saves you from needing any additional dependencies by allowing you to include the GraphiQL in-browser editor directly into your ASP.NET Core application via middleware, allowing you to explore and test your GraphQL endpoint with ease.
The GraphiQL.NET Auth middleware can be found on NuGet here
You can install GraphiQL.NET Auth by copying and pasting the following command into your Package Manager Console within Visual Studio (Tools > NuGet Package Manager > Package Manager Console).
Install-Package GraphiQLAuth
Alternatively you can install it using the .NET Core CLI using the following command:
dotnet add package GraphiQLAuth
Once installed you can add GraphiQL.NET to your ASP.NET Core application by adding the app.UseGraphiQl() middleware to the Configure method within your Startup.cs file.
Note: Be sure to call UseGraphiQl() before UseMvc().
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseGraphiQl();
app.UseMvc();
}After that simply navigate to /graphql in your browser to start using GraphiQL.
By default GraphiQL lives on the aforementioned /graphql endpoint, however it can be changed by passing your chosen path to the app.UseGraphiQl(); entry point method:
app.UseGraphiQl('/whatever/graphiql');You can also specify GraphiQl endpoint independent of your GraphQL API, this is especially useful if you're hosting in IIS in a virtual application (ie myapp.com/1.0/...) or hosting API and documentation separately.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseGraphiQl("/graphql", "/v1/yourapi");
app.UseMvc();
}Now navigating to /graphql will display the GraphiQL UI, but your GraphQL API will live under the /v1/yourapi route.
You can specify an authorization mutation to request a bearer token from. When specified users will be able to request a bearer token through the graphql API. In order for this behavior to work the graphql API must have the specified mutation setup.
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory)
{
app.UseGraphiQl("/graphql", "/v1/yourapi", "login");
app.UseMvc();
}Now navigating to /graphql will display the GraphiQL UI, but your GraphQL API will include an additional login area at the top of the screen. After a successsful login the bearer token will appear in this area.
All future graphql requeusts you make will include the token displayed in the login area. If you do not wish to login through user credentials, a valid bearer token may be copied into the login area.
- This fork only supports user credentials (username and password) when logging in. Feel free to fork and expand my solution for your needs.
- The bearer token displayed in the login area will be included in the request header. It is up to you to utilize that in your graphql API.
- The auth mutation must be part of the graphql API that you configured above.
- The auth mutation must support
accessTokenin it's return type. - The auth mutation MAY support
expiresin it's return type. When supported, the access token will be stored as a cookie for theexpiresduration.