How to compute time complexity for Deep learning models ? (can be reused for other machine learning algorithms)
The objective is to build a library to be able to estimate time complexity of machine learning algorithms.
In data science to be able to compare and analyze the necessary time to compute and get result out of machine learning models can be difficult and hazardous.
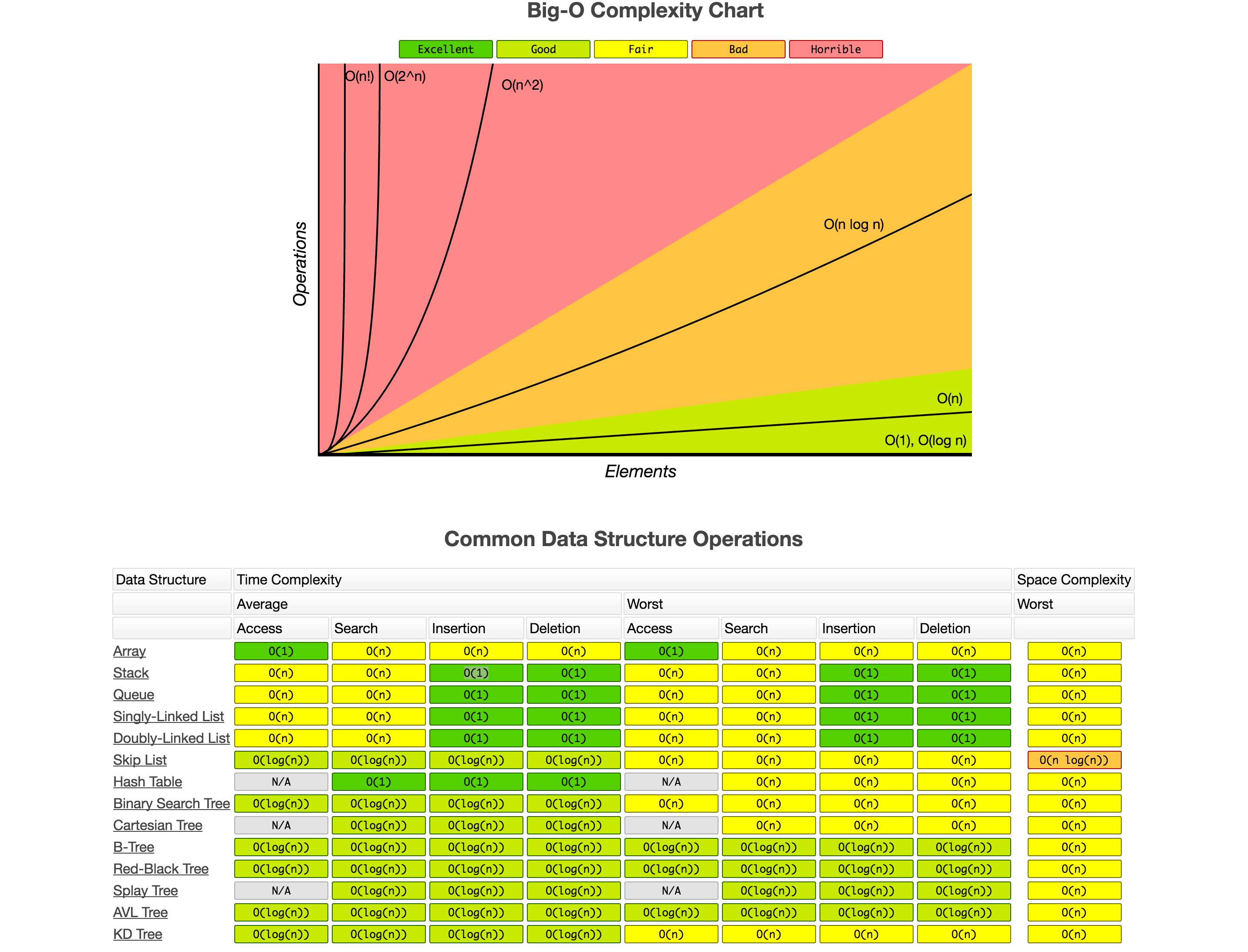
What we find on the internet regarding machine learning time complexity is more related to Big O and Big Théta computed on Operation Algorithms that are basically sub-algorithms that are used to build machine learning algorithms. No one has time or energy to re-estimate each machine learning algorithm Big O based on sub-algorithms.
The idea in this repo is to be able to estimate machine learning algorithm time complexity by computing several combinations of hyperparameters and training data matrices size (# of features and # of observations). The objective is after timing each combinations of possibilities to map it in a log linear function.
To narrow down the problem, we are focus on deep neural network structures. We define a classification problem with C classes (C is variable).
Two approaches for the moment :
n : Number of observations
p : Number of features
l : Number of layers
dropout : With Regularization ?
o : Number of Classes
n : Number of observations
p : Number of features
l : Number of layers
Based on the analysis performed:
-
With no surprise, number of features has no incidence on the time computing of a deep learning algorithm. This insight is quite logic and full of sense regarding how deep learning and representation learning concept works.
-
Number of layers has a very high incidence on time computing of a deep learning algorithm.
-
Adding a regularization has a positive incidence on time complexity. However, the confidence level of this insight is very low, as the p-value is not significant in this result. More analysis should be performed to prove the impact of regularization on time complexity.
Ideally all the computational results should be compiled to get a set of functions that can allow any data scientist to be able to estimate computational time of problem before running a training session of an algorithm.
https://www.thekerneltrip.com/machine/learning/computational-complexity-learning-algorithms/