-
Notifications
You must be signed in to change notification settings - Fork 0
How to interpret CroCoDeEL's results
In the case of related samples, e.g. longitudinal samples, animals raised together, CroCoDeEL may flag them as contaminated. To remove these cases, it is necessary to refer to the metadata of the cohort in question.
In the case of non-related samples, it is necessary to inspect scatterplots of each contamination event to discard potential false positives.
To decide whether or not contamination has occurred, there are a number of criteria to consider:
The contamination line must be a straight line, not just a bunch of points, such a these cases (Fig a & Fig b).
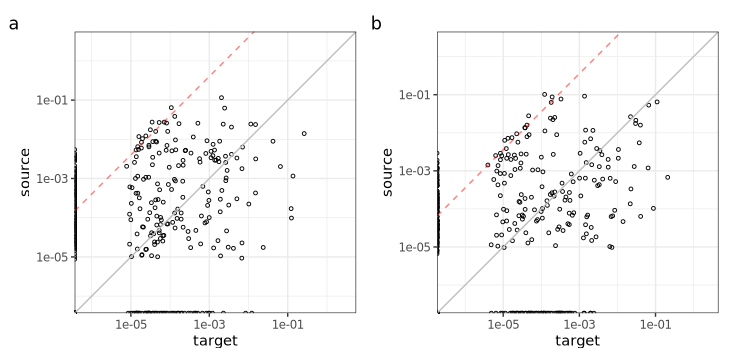
If this number of points is low (less than 10, for example), then the line may result from a random event, such a these cases (Fig a and Fig b).

In the event of contamination, all the abundant species present in the source of contamination (above a certain threshold) must be present in the contaminated sample. So if there are source-specific species with a high abundance not present in the contaminated sample, then it may be a false positive.
During contamination, there should be no points above the contamination line, in theory. However, there may sometimes be points, particularly in cases of cascade contamination. In these cases, a few points may be tolerated.
For example, here is a case of cascade contamination. Sample2 is contaminated by sample1, but points appear above the contamination line (Fig a). Sample1 is in fact also contaminated by another sample (sample3, Fig b). This other contamination explains the dots seen above the contamination line. If sample1 is processed again (sample1_new), it is no longer contaminated by sample 3 (Fig c), and the points above the contamination line disappear (Fig d).

When a case contains points above the contamination line, it can therefore be interesting to see if the source of contamination is subsequently contaminated by another sample.
Where possible, it may also be useful to link the CroCoDeEL results with the plate plans (during DNA extraction and sequencing).