Demonstration of a Database assisted Shared Access System for Rotating Radars and Wireless Communications
To provide more frequency spectrum for smart wireless devices and new things in the IoT, there is an increasing research interest in systems that facilitate spectrum sharing between radars and wireless communications. We will demonstrate real implementation of a database assisted shared access (SA) system for rotating radars and wireless communications. Our implemented SA system includes: 1) a real-time rotating radar emulator which has been designed to generate real scanning patterns of three different rotating radar systems; 2) a real-time MySQL database which assigns rules for SA-based spectrum access; and 3) A real-time FPGA-based prototype of wireless users using frequency spectrum on SA-basis. The prototype is implemented on WARP (a scalable and extensible programmable wireless platform) nodes .
Using real measurements of radars’ spectrum usage, MATLAB mapping toolbox, MySQL software and Wireless Open-Access Research Platform (WARP) nodes, we combine powerful data, software and hardware related tools to implement a real-time database assisted shared access (SA) system between rotating radars and wireless communications. In the demo, a spectrum access system obtains real-time spectrum usage information of rotating radars in an area and based on this information wireless users (WARP nodes) intelligently adapt their physical layer parameters to enable interference protection to radar systems, and to also allow a large number of wireless transmissions for SA users.
Using the collected spectrum usage/scanning patterns of the measured radar systems we have implemented a real-time emulator in MATLAB. The MATLAB-based emulator utilizes the mapping toolbox of MATLAB which is an app for analysing geographic data and creating map displays. The emulator displays a region around the city of Oulu where the three radar systems are located, it also displays the approximate locations of each radar system, real-time scanning of each radar, three geographic zones of sharing around each radar, and the locations of active users operating in the area of interest. The emulator is ported to a MySQL database to which it sends periodic scanning rates of the three radar systems.
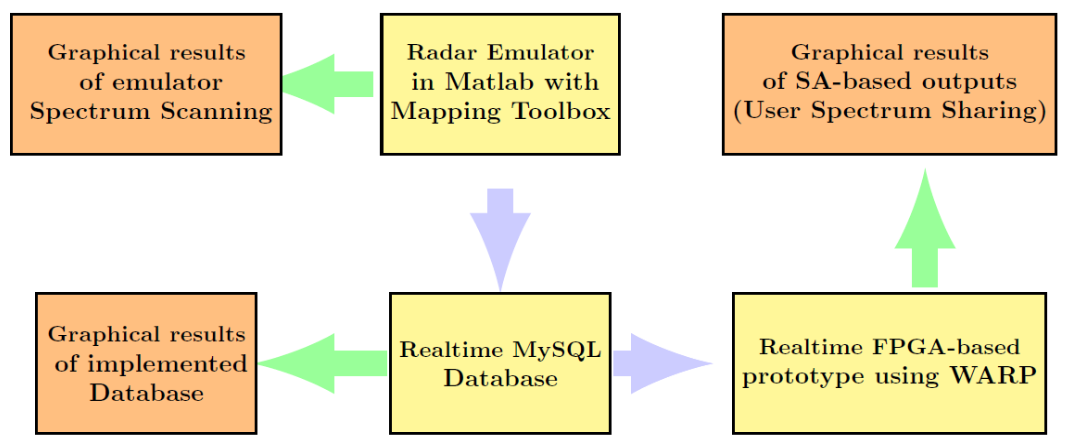
The database is implemented using the MySQL server software. The database is connected to the radar beam emulator and it is programmed to store user IDs and their latitudes/longitudes information. Based on this information, it calculates zone information, location slice index Si. The database is ported to the nodes communicating wirelessly which are implemented on WARP platforms.
Wireless users using OFDM physical layer and accessing the 20MHz channel following SA-based rules is implemented using the Wireless Open Access Research Platform (WARP) boards. At the heart of this design is a Xilinx Virtex-family Pro FPGA. This family of FPGAs is very well suited for the real-time DSP-intensive operations required by SA algorithms. Real-time events showing successful implementation of access based on temporal sharing with a rotating radars system will be demonstrated for eWINE Challenge. The outputs of successful implementation will be graphically demonstrated using a realtime spectrum analyzer manufactured by the Aaronia AG.
If you want more information, then your can refer to our publised paper. In addition, if you find any information in the content that is help for your research, then please cite the paper in your work.
Khan Z, Lehtomäki JJ, Aguilar-Gonzalez R, Vuohtoniemi R, Hossain E, DaSilva LA, Marshall A. Database-Assisted Distributed and Cloud-Based Access Methods for Unlicensed and Radar Bands. IEEE Transactions on Cognitive Communications and Networking. 2017 Sep;3(3):404-19.
