About • Get • Install • Set • Support • License
|
An introduction to my methods of configuring the Windows operating system without all of the bloat and annoying features whilst trying to keep it stable and functional in all scenarios. The chosen options should be up to everyone's preference and according to the computer's configuration. |
Linux got as on par alternative to Windows in terms of customization, and more so as time goes by. The latest versions of Windows are sometimes very cumbersome, full of bloat, and forcefully dumbed down. By comparison, these Linux interfaces (Cosmic, KDE, Gnome and so on) are getting better and better, with increasingly new features and fixes. It is also worth noting that Linux is supported by more communities and corporations including Valve with their Steam Deck. Apps wise, the compatibility mostly matches the one of Windows via tools called Wine (Windows calls translation) and Proton (Wine gaming focused). It's also worth noting that if there's an older application that doesn't work anymore on Windows, it will mostly work here.
Some Linux variants, namely distributions, are as follows: Linux Mint (Edge), by default isn't that complex or shiny but it is very stable, GUI oriented, and user friendly, plug and play type; Pop!_OS, it is distinct, elegant (Cosmic UI) and it is an easy experience, yet it is cautious about adopting zero-day updates; openSUSE Tumbleweed, professionally backed, powerful, rock-stable and very intuitive on its own, up-to-date yet auto QA tested packages, has a lot of complex GUI tools but requires a little experience in tinkering it at first (e.g. enabling non open-source repositories if desired); Fedora, professionally backed with a modern experience, early last-gen adopter so on edge cases it may be buggy; EndeavourOS, community based, made on top of a complex core (Arch), has some elementary UI tools such as installer and helper - mostly terminal centric, advanced users oriented; CachyOS, small community, based on Arch too, snappy, implements custom optimizations and schedulers, due to its nature may be unstable at times.
Important
Using Linux might be fair simple but you should have at least a minimal experience in following tutorials, as at times, the Terminal may help you because not everything is going to work as expected. It is likely to be used at least some times in the entire OS lifetime.
First and foremost, you must obtain the .iso image file of Microsoft Windows. There are more variants to choose from:
- Unofficial pre-built images:
- Assembly based on the original Windows Unified Update Platform, with minimal modifications, such as disabled system requirements check and account creation, integration of the most recent updates, SmartFix and Microsoft DaRT.
- Multiple custom builds, be they touched or untouched, including modifications such as disabled system requirements checks or even total reskins (be careful).
- Official images:
- Microsoft Software Download Listing iso media grabber for bootable USB.
- Official Windows Installation tool/iso for bootable USB or DVD.
- Fido PowerShell download script with automated access to the official Microsoft Windows retail server. There are no modifications at all.
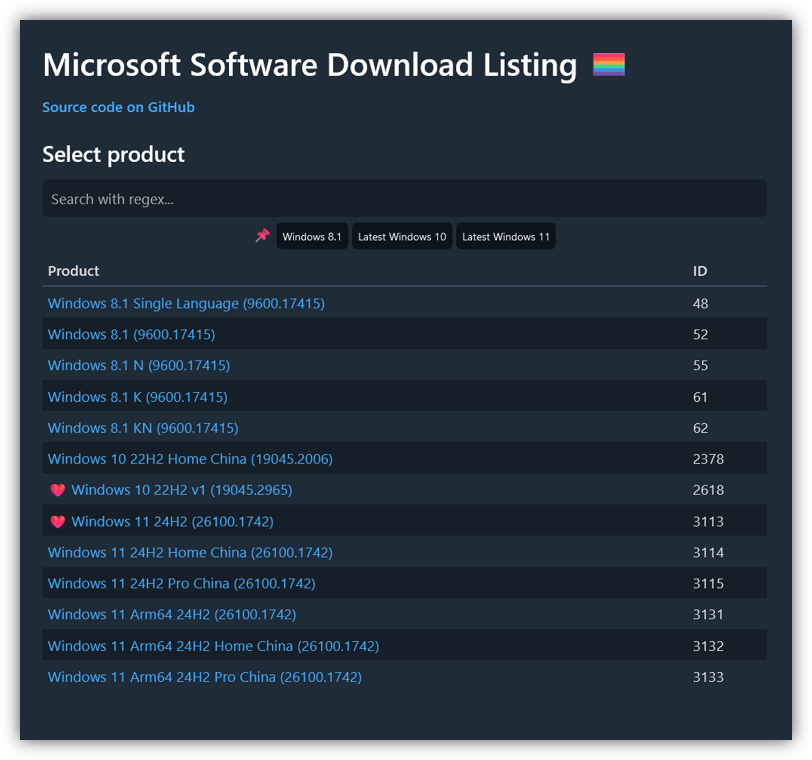
Microsoft Software grabber listing
-
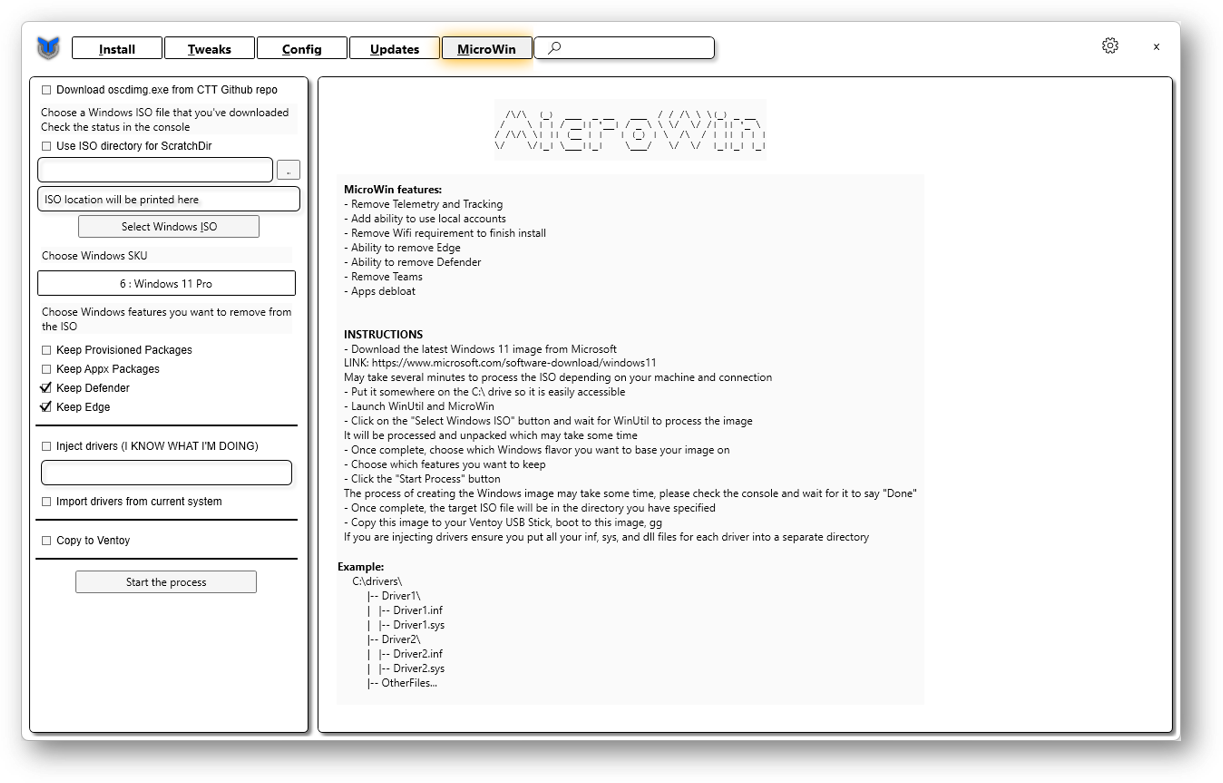
By using these images, one can apply debloat and enhance functionality which goes as MicroWin (Recommended). Or otherwise, for a simpler complexity, AtlasOS should represent a good choice as a pre-patched solution.
If the .iso image file has been completed, now is the time to create a bootable flash drive. In order to do this, you'll need an utility. There are several ways:
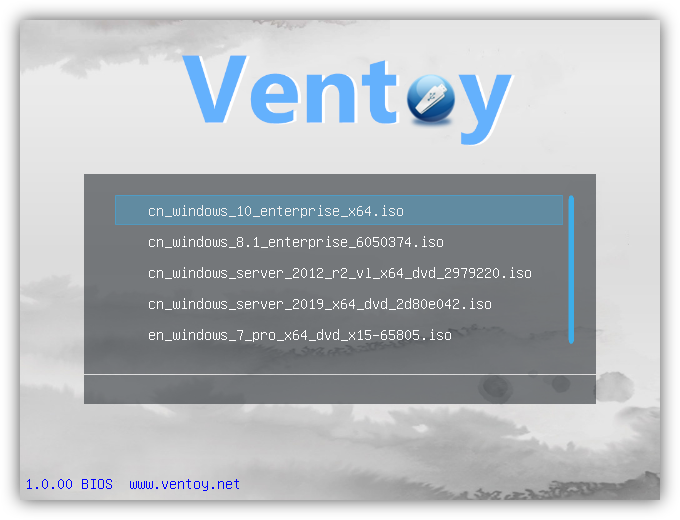
- Ventoy is a utility that creates a bootable USB, by directly booting the .iso file without the need for the USB to be formatted. Very rarely it can be bugged.
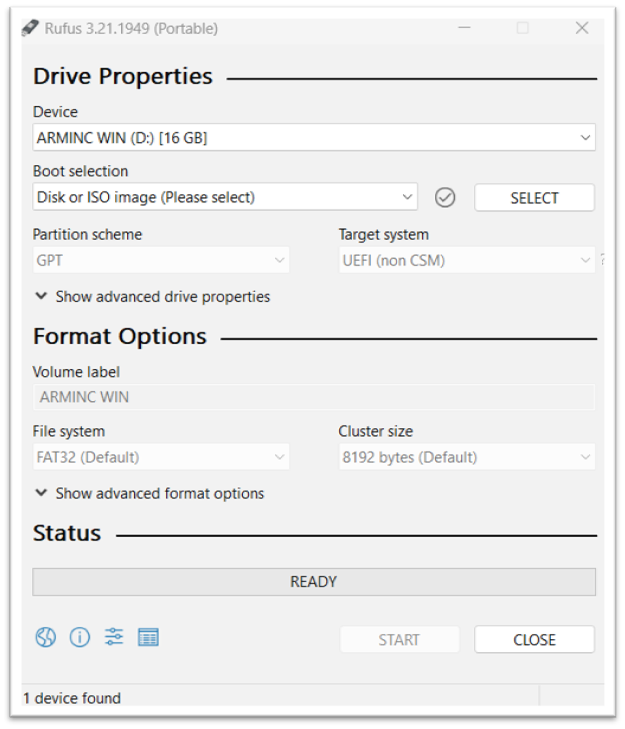
- Rufus is a utility that creates a bootable USB, by burning the .iso file.
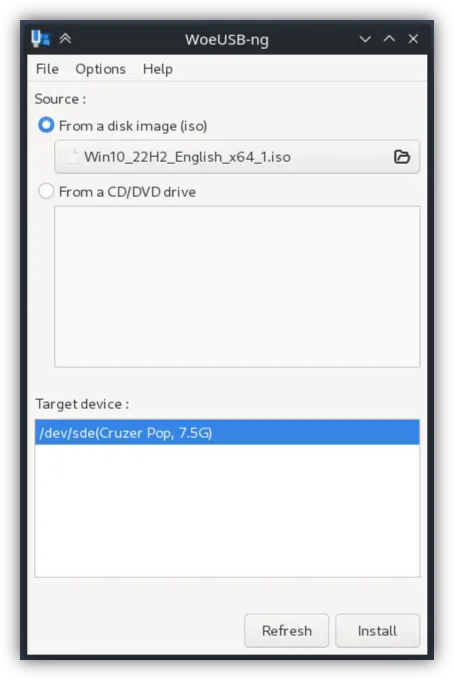
- WoeUSB-ng is a Linux-direct alternative for Rufus. It alows the creation of stable, bootable Windows ISOs for multiple distros.
Depending on the chosen settings, the application may ask if you want to stop the Windows requirement checks.
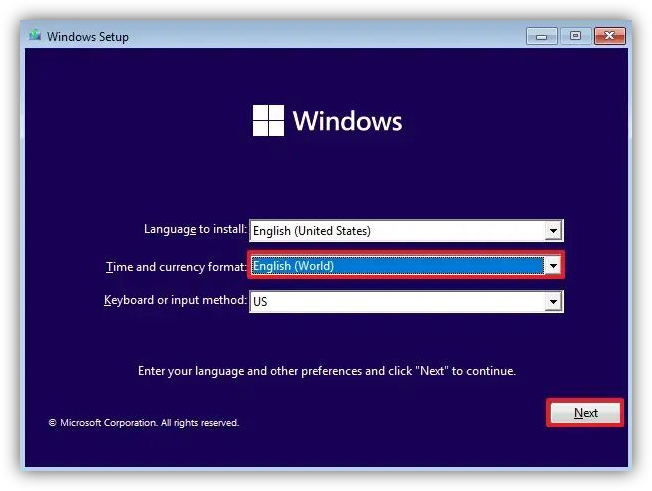
During the boot, if desired, select an EEA country from the Time and Currency format. This will recognise the installation as a Windows Digital Market Act complied version, which shortly, it is a unbloated version. Also, MSEdgeRedirect tool can be used for already existing installations, which changes them to Europe Mode. Another tool is ViVe.
Alternatively, although not so effectively, select World from the Time and Currency format. This will proceed with the installation of the operating system without third-party application links in the Start menu. During the setup, configure the out-of-the-box experience (OOBE). In case you encounter the "Something went wrong" error while the wizard attempts to load the region settings, proceed by using the Skip button to bypass the error. Be aware, after installation, you may need to set the Country or region values in settings.
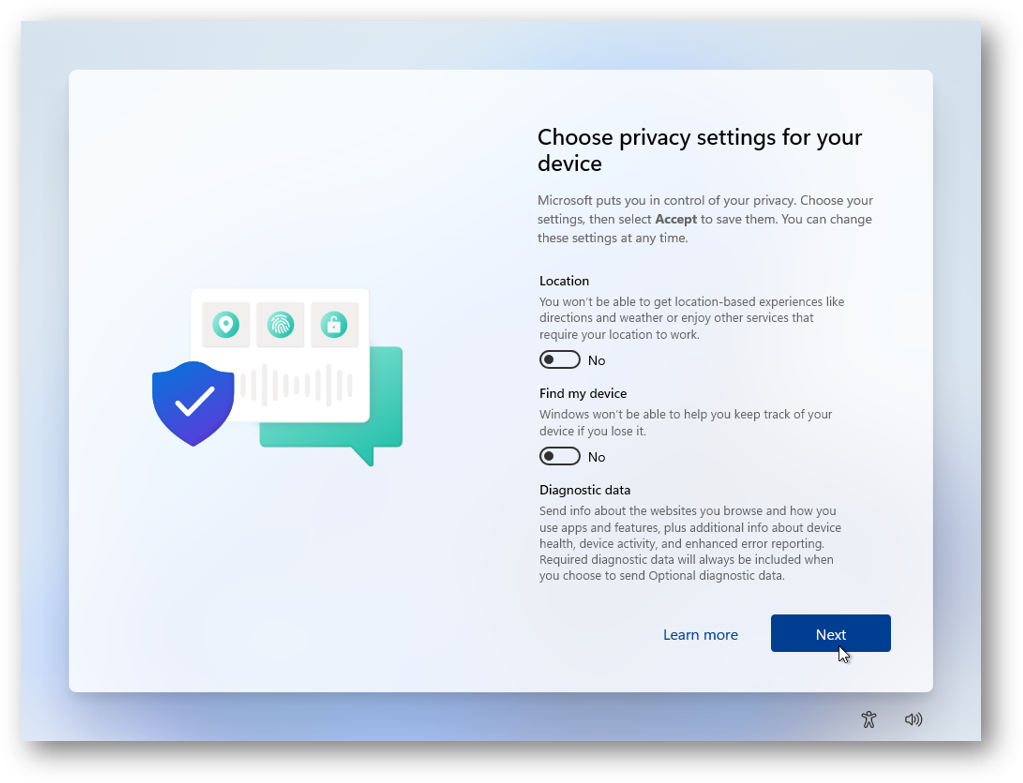
Near the end of the installation, if you haven't downloaded a pre-built image with sequence skip, you will be asked about privacy preferences. Try to disable/reject them. Also, try to avoid connecting the device to the Internet during the setup.
If you are done with it, now you should prepare the operating system.
The first thing on the list is to try and change the browser. Zen or unforked Firefox are the most optimal variants, even speaking of extension capabilities. About that, see my uBlock Settings. Check other extensions too.
Next, for all the other steps, you'll need a file archiver. NanaZip, unforked 7-Zip/ or even PeaZip should do it. These are open-source.
For peace of mind, it is a good habit to install an antivirus. Depending on your Windows image, the default one, Defender should be good enough. In other considerations, it may be removed, disabled, or not working at all. As options there are Kaspersky Security Cloud (Free) or even BitDefender (Free). Kaspersky has almost nearly protection module of its premium counterpart, and it is intelligent enough to disable itself when resources are required, such as during gaming.
Now, check all available updates and drivers, install them, and restart the computer. Ensure there are no remaining updates. It is not advisable to disable or avoid them.
Then, if desired, do the same for Windows Store, and only after that, disable its auto updates.
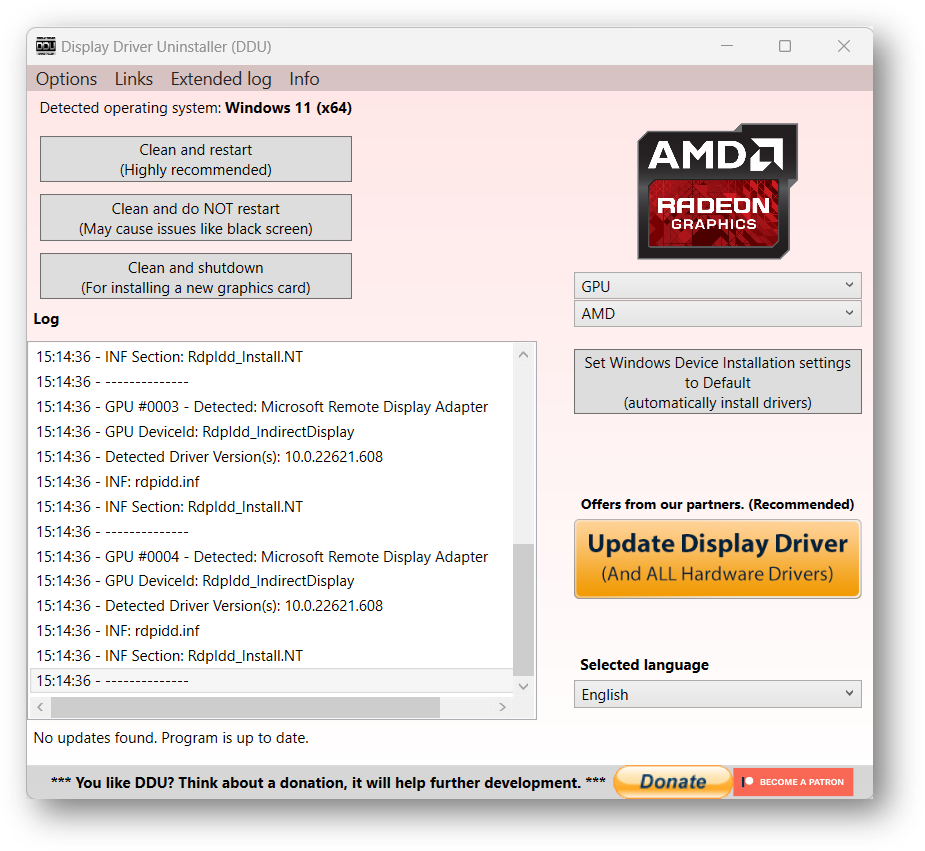
At times, the main (e.g. graphical) drivers shouldn't be installed through Windows Updates, so it's recommended to reinstall them through official means. To uninstall them, use Display Driver Uninstaller, where you should check all "remove" specific options, and also very importantly, check the Windows Update prevent download option. Uninstall every component, restart, and find the latest official installers (AMD/NVIDIA/INTEL).
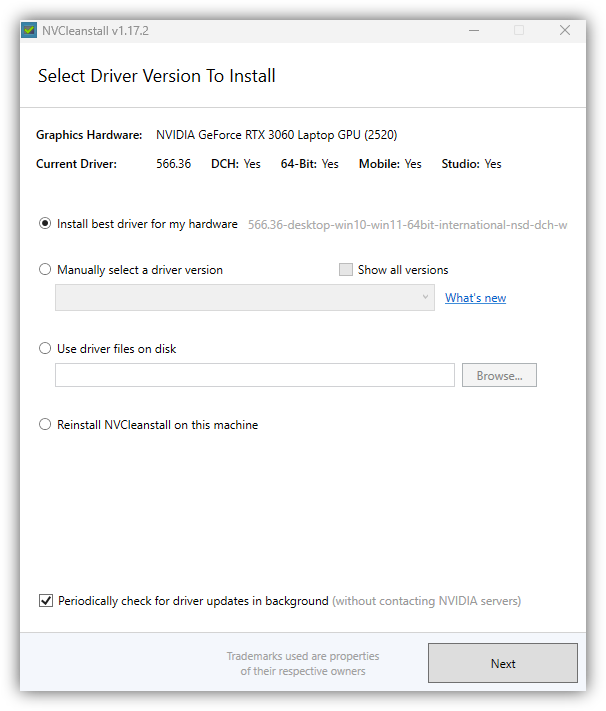
If your computer has a compatible NVIDIA GPU, you could try NVCleanstall, which is a tool for more customisable capabilities, bloat-free graphical drivers.
- Let it auto-detect the recommended drivers. You should double-check.
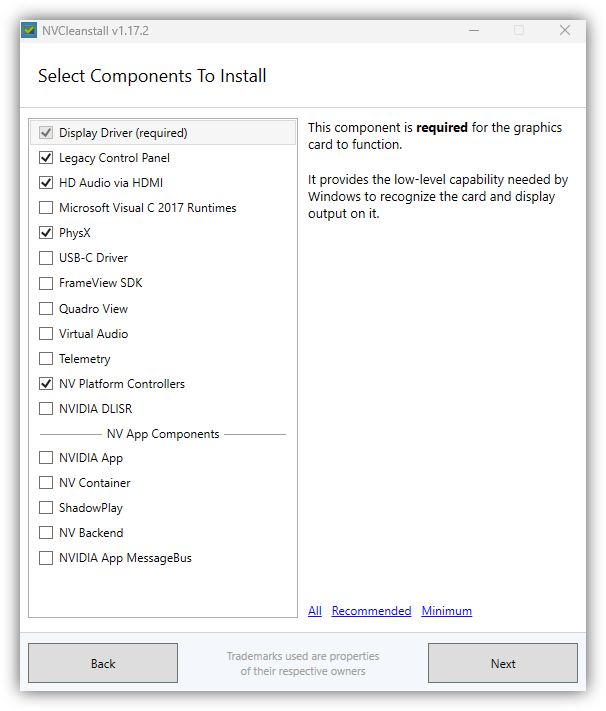
- Select the Recommended components if desired. It depends on the type of computer and your preferences. For laptops, Optimus is somewhat required.
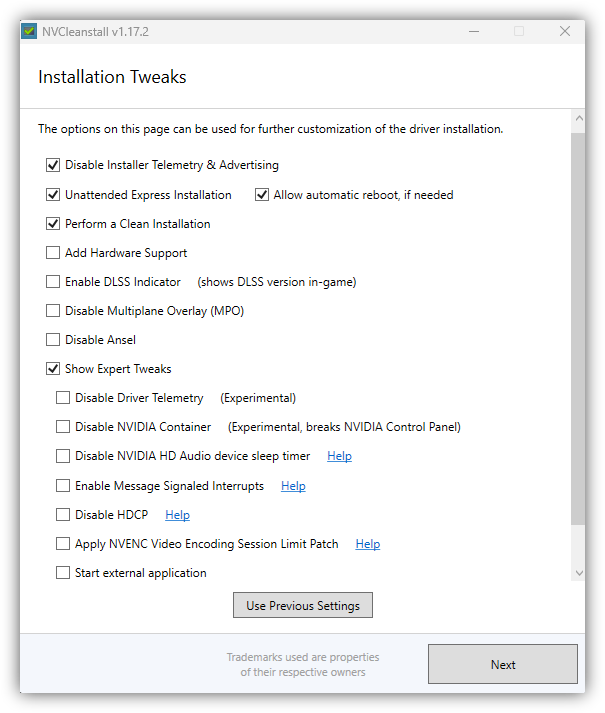
- Then, for the tweaks, set the preferred ones. You could disable the telemetry, disable custom type of install altogether (make it faster), clean the older driver traces (not required if uninstalled through DDU), add support for custom/older hardware, enable the DLSS version indicator, disable MPO (which has to do with a technique that allows different user interfaces to be displayed on the screen at the same time and appear as if they are layered on top of each other) - it is usable for stable windowed resolution apps, and so on. It's useful but somewhat buggy in older versions, newer drivers should do it just fine. If something is wrong, e.g., there are crashes or slower experiences, this could be a reason, and if so, try to disable it. You can disable Ansel too, which is a in-game screenshot tool.
There are also some advanced settings that could break or mess with the drivers, and some of them even need repackaging and a new signature (incompatible with some anti-cheats). It is able to disable some in-driver telemetry, disable process containers (see task manager), disable the buggy audio timer (not useful if there is no HD Audio component), enable MSI (it allows computer components, be it a GPU, to directly send interrupt messages to the CPU, bypassing the PIC, which improves efficiency and reduces latency) - older NVIDIA GPUs didn't have this feature enabled by default. The newest models available probably have it enabled (manual check is required). Also, it could disable HDCP (which is a digital copy protection module - some apps and streams will not allow their usage without this one), enable custom patch for nvenc video encoding (in day-to-day usage, the patch is beneficial for users who frequently work with video encoding tasks or streamers who need to encode multiple video streams at the same time).
- When the installation is complete, there are some settings to adjust.
The primary objective is to enable applications to use their own settings and not be obligated. Techniques established by drivers can occasionally cause instability. Generally, only something that can be externally enabled should be utilized. Any extra settings (such as Low Latency Mode) should be tailored for each application on a per-application basis (in 3D Settings > Program Settings).
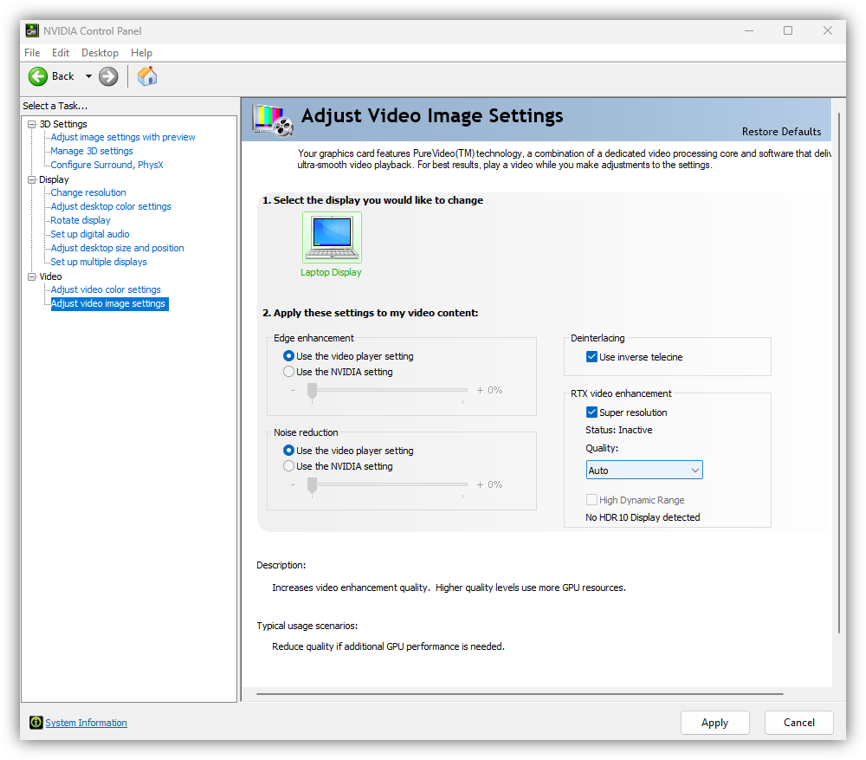
- After everything is set, there is another thing to do. Toggle RTX Video Super Resolution, which is a technology that uses AI to upscale lower resolution video to near-native quality.
VSR works by using the Tensor Cores to analyze each frame of the video and then reconstruct it at a higher resolution. This process is done in real-time, so there is no need to pre-render the video at a higher resolution. Some disadvantages of VSR include limited support in video players, potential compatibility issues with certain videos, and the possibility of introducing artefacts, especially during fast-moving scenes.
Therefore, first, enable Use advanced 3D image settings and then proceed to Global Settings.
| Feature | My setting | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Image Scaling | OFF | An upscaling technology that is less computationally expensive but has worse image quality than DLSS. Driver function. Works in all games, and no special hardware is required. |
| Ambient Occlusion | OFF | Adds subtle shadows and shading to the areas where objects or surfaces meet and to areas that are not directly lit. Better set up directly by the application. Can be used for games that are too old to implement this feature by themselves. |
| Anisotropic filtering | Application-controlled | Improves the quality of textures (enhances their smoothness to make them appear sharper) on surfaces that are viewed at an angle. Noticeable on textures that are seen at a steep angle, such as walls or floors. Without it, textures can appear blurry and pixelated. Sometimes it is relevant to enforce high texture filtering globally (not in-game) due to potential quality issues with individual developer solutions. Also, it can be used if the game lacks a native "Anisotropic Filtering" option, has a limited anisotropic option (up to 4x AF), and supports only up to "Trilinear Filtering". |
| Antialiasing - FXAA | OFF | It smooths the jagged edges (through blurring) and flickering with less of a performance impact than other antialiasing settings. Doesn't make graphics look as smooth as other traditional methods like MSAA. May spoil the look of more text-based games. |
| Antialiasing - Gamma correction | OFF | Is a method to adjust brightness data for displays so that shown content appears more natural. Displays are not linear, so gamma correction ensures that the brightness levels match the eye's perception. This is a feature that mostly alters the image rather than enhancing it. |
| Antialiasing - Mode | Application-controlled | It determines how antialiasing is applied to games. Enhancing the application setting may improve the image quality of the game. It is recommended to let the game automatically select the most suitable antialiasing method based on your graphics card and the game's graphics settings. Otherwise, any custom settings may break or alter the graphics. |
| Antialiasing - Transparency | OFF | Can improve the appearance of transparent objects, such as glass and water, by making them appear smoother and less jagged. Requires MSAA in order to work. |
| Background Application Max Frame Rate | 30 | Controls the maximum frame rate that games and other applications can run at when they are not in focus. By limiting the frame rate, you can save power and improve the performance of your computer. |
| DSR - Factors | 2.25 (DL Scaling) | The feature allows users to render games at a resolution higher than their monitor's native resolution and then scale down the image to fit their monitor's resolution. Can lead to enhanced sharpness and more detailed visuals. DSR factors serve as multipliers that users can apply to increase their game's resolution. For instance, if a monitor's native resolution is 1080p, employing a DSR factor of 2x would enable rendering games at a resolution of 2160p. |
| DSR - Smoothness | 33% | It adjusts the sharpness or smoothness of the image, especially if there are blurry spots or jagged edges on the image. Higher values may induce a lot of blur in the background. |
| Low Latency Mode | OFF (set per individual game) | The technology reduces the delay between a user's actions in a game and the corresponding reactions on the screen. This is achieved by minimising the number of frames queued up in the graphics pipeline. As a result, the responsiveness of the games is notably improved, particularly in competitive multiplayer. When a game supports the Reflex Low Latency mode, the preference is to utilise that mode instead of the Ultra Low Latency mode in the driver. Nonetheless, when both modes are enabled, the Reflex Low Latency mode will be given higher priority automatically for the user. On value limits the number of queued frames to 1, which can reduce latency but may also lead to stuttering. Ultra minimises the number of queued frames even further, which can reduce latency even more but may also lead to more stuttering. |
| Max Frame Rate | OFF | Limit the maximum frame rate for a game or application. Can be useful for power savings, reduced input lag, and preserving the Variable Refresh Rate range. Better used by in-game settings. |
| Multi-Frame Sampled AA (MFAA) | OFF (sometimes can be set per individual game) | An anti-aliasing technique developed by NVIDIA that improves upon the quality of traditional multisample anti-aliasing (MSAA) while reducing the performance impact. It does this by using a technique called temporal supersampling. MFAA recognizes that the averaging done by MSAA can be done over time by changing sample positions in each frame and applying a filter. This allows MFAA to provide image quality similar to 2x MSAA with almost no impact on performance. The ultimate objective is to provide comparable antialiasing such that MSAA 2x + MFAA ideally achieves MSAA 4x quality at a similar performance cost to MSAA 2x. As a drawback, this function can possibly disable D3D11 Driver Command Lists, which can hinder multi-threaded rendering, resulting in decreased performance, especially when CPU-limited. Also, MFAA exhibits suboptimal performance when the FPS is already low, as it can lead to motion smearing and blurring issues. |
| OpenGL GDI compatibility | Auto | The way to render OpenGL applications. Prefer Compatible OpenGL prioritizes battery life, while Prefer Optimized OpenGL prioritizes performance. Beneficial for laptops and notebook PCs, as it enables users to choose between performance and power optimizations for OpenGL windows. Selecting either option may conflict with applications utilizing both OpenGL and GDI rendering. For laptop users, it is recommended to set it to Auto and allow the driver to determine the appropriate behavior. |
| Power management mode | Normal - Optimal Power | It dictates how the GPU behaves in relation to power usage, performance, and frame rates. Adaptive mode exhibits a smoother (nearly power-saving) linear voltage scaling compared to Optimal, where voltage is dynamically adjusted more aggressively based on in-game utilization. On the other hand, Maximum Performance mode targets the highest clock or voltage, regardless of whether it is necessary for the game. |
| Shader Cache Size | Driver Default | Stores pre-compiled shader code in the computer's storage. When a game or application first starts up, the GPU needs to compile the shader code for each shader it will use. This can take a few seconds, and it can cause the game or application to stutter or lag as it waits for the shaders to compile. With shader cache enabled, the GPU will store the pre-compiled shader code for each shader it has seen before. Drawbacks include increased computer storage usage due to storing pre-compiled shader code and the possibility of cache invalidation when changes are made to the game or application files, requiring recompilation of affected shaders. The default value is about 4 GB. |
| Texture filtering - Anisotropic sample optimization | OFF | Reduces the number of AF samples depending on the texel size (texture pixel), which is influenced by factors such as texture resolution, polygon size, and display resolution. However, implementing this optimization may result in potential side effects, including blurring and shimmering. |
| Texture filtering - Negative LOD bias | Allow | Adjust the level of detail of the textures. The LOD Bias plays a vital role in managing texture detail by influencing the selection of Mipmaps. Mipmaps consist of a set of precomputed textures, each with varying resolutions, strategically employed to enhance performance. When an individual looks at a nearby surface, the system loads a higher resolution mipmap. As the person moves away from that surface, progressively lower resolution mipmaps are displayed in response to their changing distance. Utilizing a negative LOD Bias allows the displacement of mipmap levels to a greater distance, leading to enhanced texture sharpness. However, this improvement comes at the expense of introducing shimmering effects when textures are in motion. For users not utilizing DLSS, clamping is recommended, while those employing DLSS should opt for the Allow setting (which may enhance temporal stability but can also lead to flickering and moire, which is scene content-dependent). |
| Texture filtering - Quality | Quality | A universal setting that optimizes all Anisotropic Filtering settings globally. |
| Texture filtering - Trilinear optimization | OFF | It enhances the performance of trilinear texture filtering. Trilinear filtering is a method used in 3D computer graphics to improve the visual quality of textures when they are displayed at different levels of detail or viewed from varying distances. When it is enabled, the graphics driver employs an efficient algorithm to adjust the level of detail for textures dynamically, optimizing the process and improving performance. |
| Triple Buffering | OFF (sometimes can be set per individual game) | It works by keeping three frames in the buffer at once. This allows the GPU to start rendering the next frame before the previous frame has been displayed. Aims to improve frame rate consistency and reduce screen tearing in 3D applications, particularly games. It is an alternative to double buffering, which is the default buffering method used in most games. Can be used in scenarios where screen tearing is noticeable and input lag is not a significant concern. Used in combination with V-Sync. |
| Vertical sync | Use the 3D Application setting (set per individual game) | Synchronizes the frame rate of a game with the refresh rate of the monitor. This helps to prevent tearing, which is a visual artifact that can occur when the game is drawing frames faster than the monitor can refresh. The game will only render frames when the monitor is ready to display them. This can help prevent tearing, but it can also introduce input lag. If the FPS drops significantly below the monitor's refresh rate, V-Sync can cause stuttering. |
| Virtual Reality pre-rendered frames | 1/Use the 3D Application setting | Controls the number of frames that are rendered ahead of time in VR games. A higher value can help improve performance and reduce stuttering in VR games. Also, a higher value can induce dizziness. |
| Virtual Reality - Variable Rate Super Sampling | Adaptive | Dynamically adjust the super sampling level in VR games. This can help improve performance and reduce stuttering without sacrificing image quality. VRS works by rendering different parts of the scene at different levels of detail. The parts of the scene that are in focus are rendered at a higher level of detail, while the parts of the scene that are not in focus are rendered at a lower level of detail. Always On value uses a fixed super sampling level for all frames. This can provide better image quality, but it can also reduce performance. |
| Vulkan/OpenGL present method | Auto | Controls how Vulkan and OpenGL games are rendered. Prefer layered on DXGI Swapchain value utilizes a layered DXGI Swapchain for rendering Vulkan and OpenGL games, potentially improving performance but causing stuttering. It treats Vulkan and OpenGL games as if they were DX12 in the final output. While they are still rendered and processed using their original API, the frames are displayed on the monitor through DXGI, allowing Microsoft's new fullscreen optimizations (flip model) to be applied to these APIs. Moreover, Multiplane Overlays (MPOs) can be assigned to Vulkan and OpenGL applications for windowed mode direct present to the monitor, resulting in tearing with v-sync off in windowed mode and reduced input lag overall. Prefer native on DXGI Swapchain value uses the default native DXGI Swapchain, generally considered the best choice for most users. |
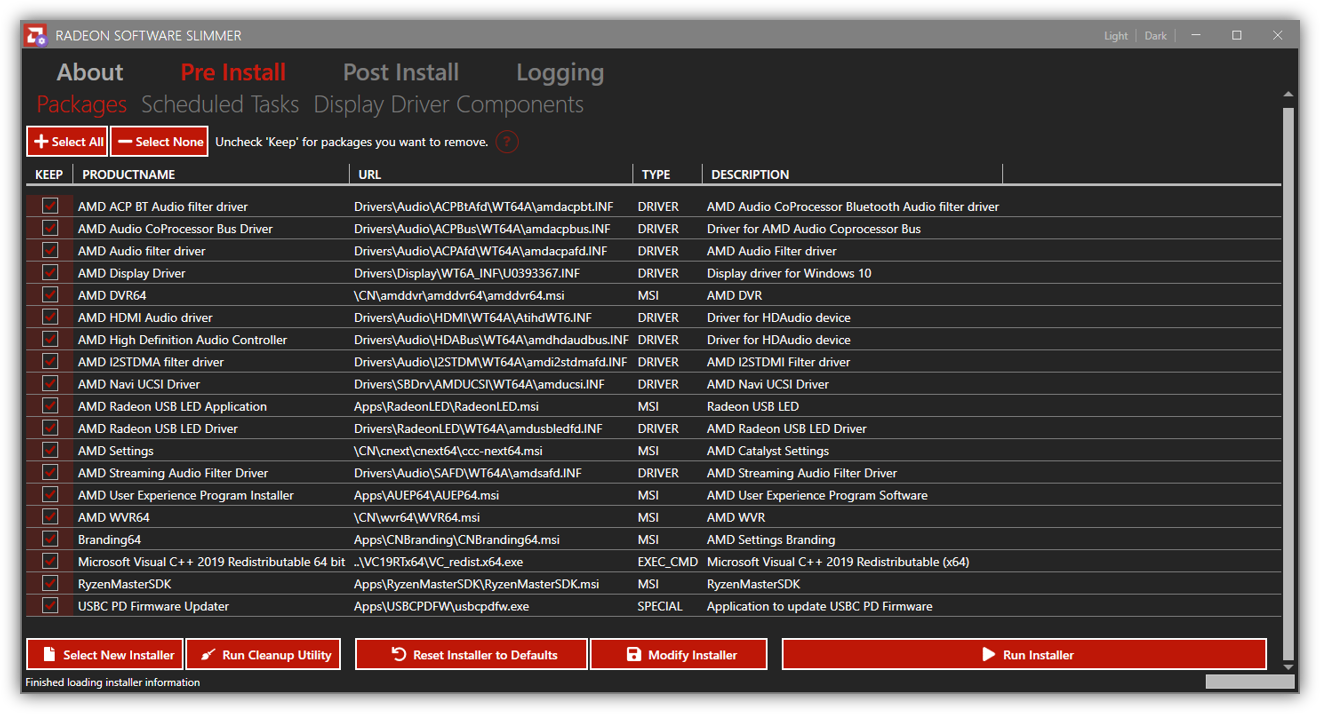
Furthermore, for AMD-enabled GPUs, there is no identical replacement. Their official installer has very few bloated components, making it unnecessary to unbloat it. But still, the closest available alternative in terms of operating mechanism would be RadeonSoftwareSlimmer, which is pretty straight-forward.
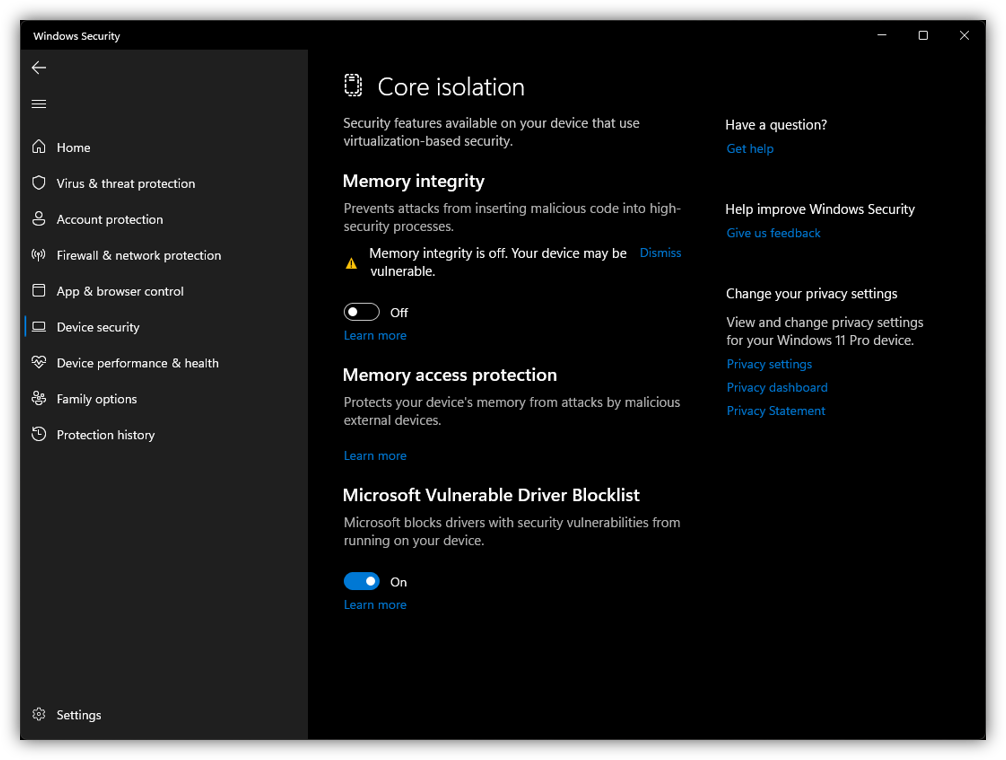
Additionally, based on preference, Memory integrity (Core Isolation) could be disabled. It's a feature of the Windows operating system that helps protect the computer from malware attacks. It does this by using hardware virtualization to create a secure area in your computer's memory where important system processes run. This area is protected from malware that attempts to modify or inject code into it. Its downside is that it can have a negative impact on performance, especially when running demanding applications.
In addition, don't forget to activate Windows and other components.
The default Taskbar, Start Menu, Context Menu, and File Explorer experiences are regrettable. StartAllBack is enhancing all elements organically. Unfortunately, the animations don't have the same fluency and are sometimes prone to bugs. If you don't want to, you can try other alternatives, such as just returning to the complex context menu through Winearo Tweaker.
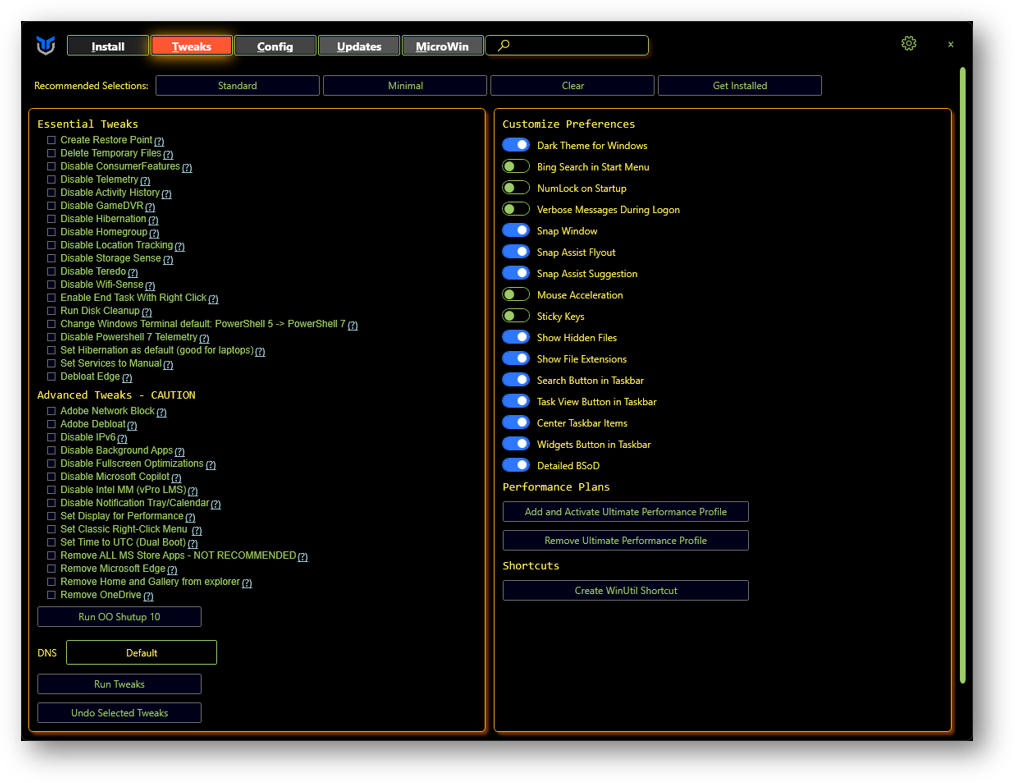
Above presented Winutil has a tweak component too. So, it can and should be used to enhance the operating system. If it was used through MicroWin, some are already applied, such as Minimal (e.g. disabled consumerfeatures, telemetry, services). In this case, the user still has the to tweak it even more if desired.
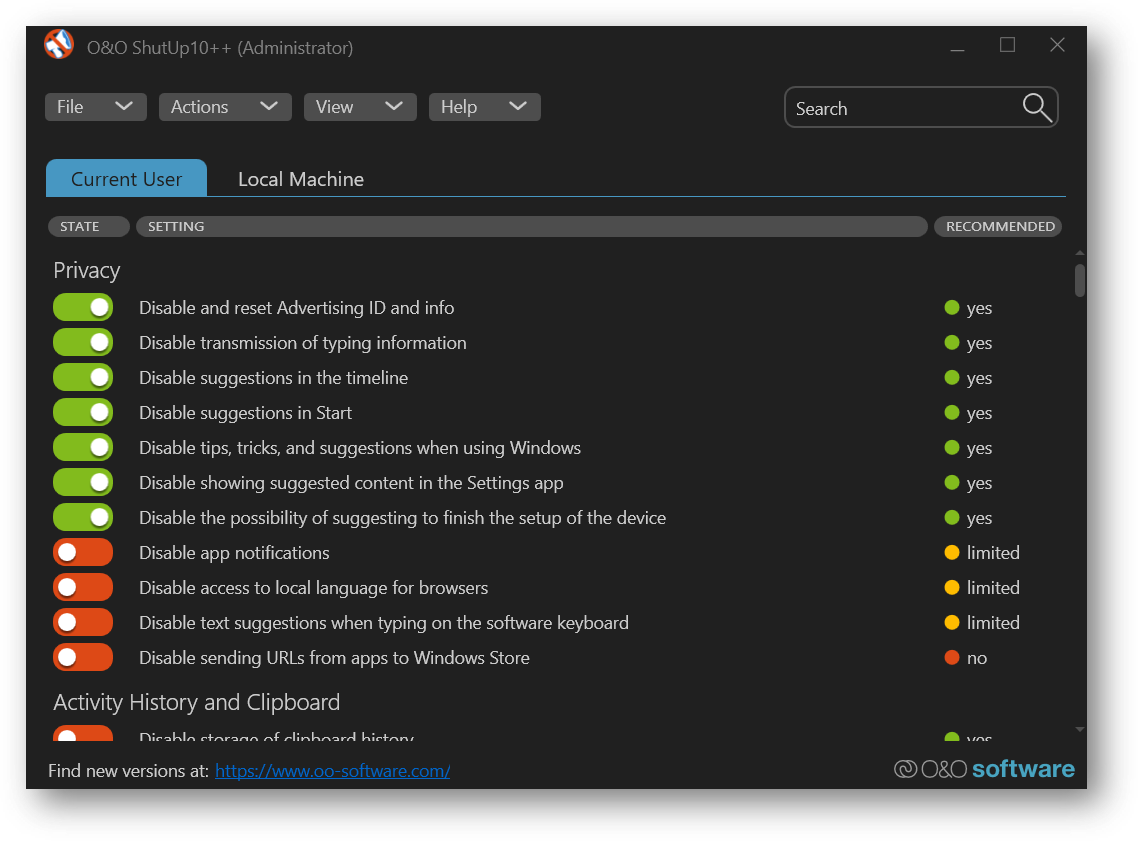
If there was no tool used, the first part of debloating is going to be through O&O Shutup. It can tweak most of the usual settings. Here is my exported example configuration... Disabling every feature can lead to compatibility errors.
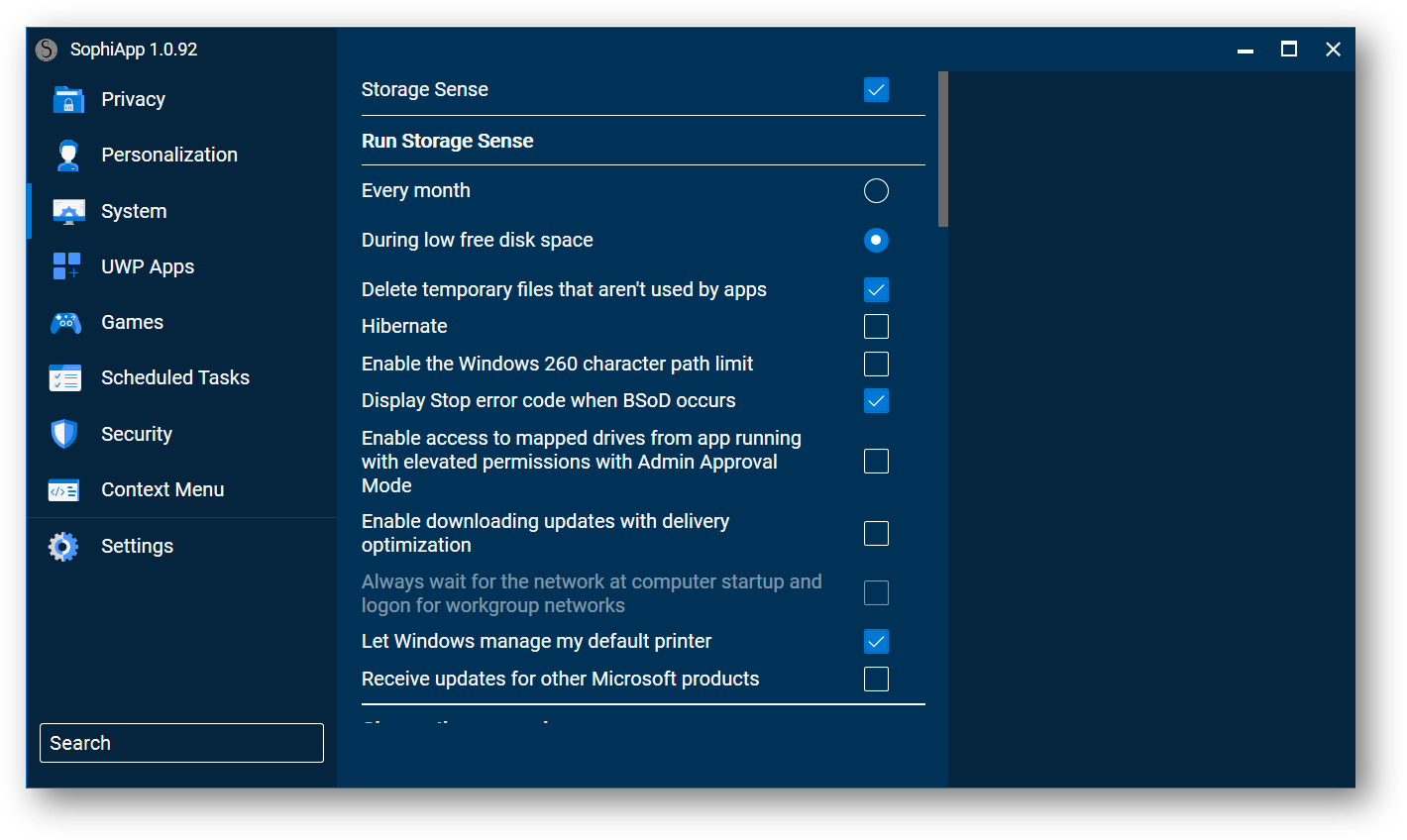
The second part via goes with SohpiApp. It has more comprehensive settings. You can deactivate some unnecessary services that are not needed and even remove UWP apps. Uninstalling unnecessary apps (e.g. help, maps) should be fine, but refrain from the complex ones associated with the operating system, such as Edge, Cortana, or Xbox, if not needed. Nowadays, Windows is so integrated that it will be challenging or almost impossible to use it in this way without encountering any errors if not experienced or using last-day tweakers.
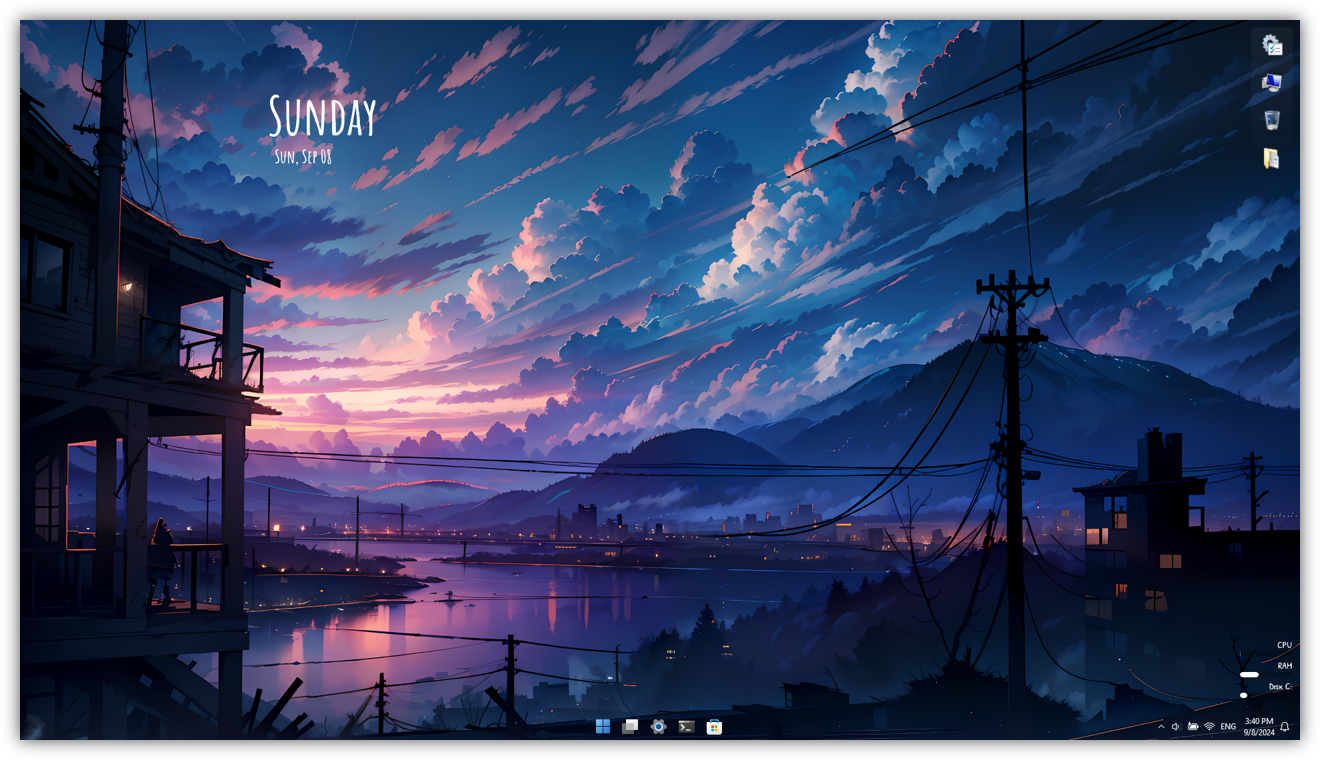
Furthermore, the desktop interface may be personalized. For instance, consider attempting a minimalist approach to simplify its workspace.
The first part includes taskbar configuration as previously discussed. StartAllBack should be installed and configured as desired. In this case, a Proper 11 theme, with Default visual style, at M icon size and XS icon margins should do it. On top of that, centered task icons, together and dynamic transparency may be utilized. As a substitute, ExplorerPatcher can be used.
Next, the further step will consist in downloading of RainMeter customization tool. It allows enabling different design modules, called 'skins' on the desktop workspace. Templates may be found here.
The lake landscape wallpaper can be downloaded here. Now, the date and time skin used is River. It has a manually placement near top-left area. You may install the font from skin's @Resource directory (see the folder path from manager). The included resource monitor is placed at bottom-right. The shorcuts such as 'This PC', 'Recycle Bin' aren't used in their classical way but, instead, are used in a fancy Quantum dock. Now, this one is (even more) customizable through an configuration file. Don't forget to disable the default icons on the Desktop at Settings > Personalization > Themes > Desktop icon settings. The icons are custom (must be placed in correct directory). Dock's preset configuration may be directly replaced with the custom one. Optionally, the River skin has as default drive, the Disk D: instead of C:, which is the most common one. Get the modified config here.
At the end of customization process, do open the RainMeter manager and for each skin .ini file, disable the draggable attribute to avoid messing them up. Even more, to avoid having the desktop files, if renamed or modified, automatically placed in the dock's corner space by Windows, go to Settings > Personalization > Start and deactivate 'Show recently opened items in Start, Jump Lists, and File Explorer' option.
The start button, called 'Orb' may be modified using a specialized tool. StartAllBack has the function too. Currently used Orb is called Sphere.
Some other models can be found on generic deviations or in gallery. Please be aware that the required orbs aren't some generic pngs, but rather a three layer state image.
These apps are optional, or some of them may be included in the operating system.
- Microsoft Visual C++ Redistributable
- Microsoft DirectX Legacy
- .NET Framework 3.5
- .NET Framework 4.8.1
- .NET Runtime
- Java
- Revo Uninstaller or BCUninstaller
- IObit Unlocker
- qBittorent
- WinCDEmu
- Parsec
- WingetUI
- Dimmer
- !cracksurl
- WizTree or TreeSize
- WizFile or UltraSearch
- Upscaly
- Wondershare PDFelement
- VMWare Workstation
- Internet Download Manager
- !megathread_resources
- !fmhy
- Spotify-X
- Stremio
- Bluetooth Audio Receiver
- mpvnet media player - (cfg) or mpv media player and mpv menu plugin
- nomacs Image Viewer
- Bitwarden or Proton Pass
- Translate Web Pages
- Location Guard
- FastForward
- Dark Reader
- Song Identifier
- Awesome Screenshot
- Reddit Enhancer
- ViolentMonkey
- Video DownloadHelper
- Absolute Enable Right Click
- Save pages - SingleFile
- Download GitHub Directory
- Twitch VOD Viewer
- Google Search Maps Button
- CanvasBlocker
- CleanURLs
- Stream Bypass
- WebDeveloper
- Bonjourr Startpage
- User-Agent Switcher or User-Agent Switcher and Manager
- Video Speed Controller
- Alternate Player for Twitch.tv
- History Cleaner and Clear Browsing Data
- View Page Archive
- Search by Image
- Enhancer for YouTube or YouTube Enhancer or YouTube Redux
- Return YouTube Dislikes
- Thumbnail Rating Bar for YouTube
- YouTooltip
- Watchmarker for YouTube
- Better YouTube Shorts
- YouTube NonStop
Reach out to me via the profile addresses.